Starting an auto repair shop can be a rewarding venture, but it comes with its own set of challenges. One of the biggest hurdles is figuring out how to price your services. Set your prices too high, and you might scare away potential customers. Set them too low, and you may not cover your costs or make a profit. This is why having a solid pricing strategy is crucial for the success of your business.
More than just about making money, pricing is about finding a balance that keeps your customers happy and your business profitable. Effective pricing strategies help you cover your expenses, pay your employees, and invest in your shop’s growth. They also allow you to offer competitive rates while maintaining a high level of service.
By the end of this article, you’ll be well-equipped to develop a pricing strategy that supports your business goals and helps your auto repair shop thrive. In the following sections, we’ll dive deeper into each of these components, providing you with practical advice and insights to make informed decisions.
Understanding Your Costs
Before you can set your prices, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of your costs. Knowing what it takes to keep your shop running will help you avoid underpricing your services and ensure you cover all your expenses while still making a profit. Costs in the auto repair business can be divided into three main categories: fixed costs, variable costs, and semi-variable costs. Let’s break down each of these.
Fixed Costs
Fixed costs are expenses that remain constant regardless of the number of customers or repairs you handle. These are the baseline expenses you need to cover just to keep your doors open. Common fixed costs in an auto repair shop include:
- Rent or Mortgage: The cost of leasing or owning your shop space. This is typically a significant portion of your fixed costs.
- Utilities: Regular bills for electricity, water, heating, and cooling. While these might fluctuate slightly, they remain relatively consistent month to month.
- Insurance: Various insurance policies, including liability insurance, workers’ compensation, and property insurance, which are necessary to protect your business.
- Salaries: Wages for full-time staff who receive a regular paycheck, regardless of the workload. This can include administrative staff, managers, and certain technicians.
- Equipment Leases: Payments for leased equipment, which remain the same regardless of how much you use the equipment.
Variable Costs
Variable costs fluctuate depending on the volume of work your shop handles. These costs increase with each additional repair job you take on. Common variable costs include:
- Parts and Materials: The cost of parts, fluids, and other materials needed for repairs. These costs vary based on the type of repair and the vehicle model.
- Labor: Wages paid to technicians based on the hours worked or the specific jobs completed. Unlike salaried employees, these costs can vary significantly depending on the number of repairs.
- Supplies: Consumable items like cleaning supplies, gloves, and shop towels. The more cars you service, the more supplies you’ll use.
- Subcontracted Services: Sometimes, you might need to outsource certain jobs to specialists or other shops. The costs for these services can vary widely.
➤ Download all the repair manuals your shop needs here!
Semi-Variable Costs
Semi-variable costs, also known as mixed costs, have both fixed and variable components. These costs can change based on your level of activity, but there is always a base amount you need to pay. Examples of semi-variable costs include:
- Salaries with Overtime: Regular wages that become variable when you need to pay overtime during busy periods.
- Utilities with Usage Tiers: While some utilities are generally fixed, certain services like electricity might have usage tiers where costs increase after exceeding a certain amount of consumption.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Regular maintenance for your shop’s equipment is a fixed cost, but unexpected repairs or increased usage can add variability.
Break-Even Analysis
A break-even analysis is a critical tool for any business owner. It helps you determine the point at which your total revenue equals your total costs, meaning you’re not making a profit, but you’re not losing money either. This is your break-even point.
To perform a break-even analysis, you need to:
- Calculate Total Fixed Costs: Sum up all your fixed costs.
- Determine Variable Cost per Unit: Figure out the average variable cost per repair job.
- Set Your Average Price per Unit: Decide on the average price you’ll charge for a repair job.
The break-even point in units (number of repair jobs) is calculated using the formula:
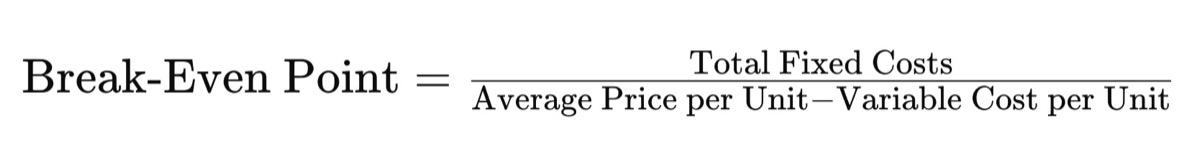
Performing this analysis gives you a clear target for the number of repairs you need to complete to cover all your costs. It’s a crucial step in setting realistic pricing and sales goals for your shop.
Market Research and Competitive Analysis
Before setting your prices, it’s important to understand the market landscape and how your competitors are positioning themselves. This knowledge will help you set competitive prices that attract customers while ensuring profitability. Here are the key aspects of market research and competitive analysis.
Identifying Your Competitors
Knowing who your competitors are is the first step in understanding the market. Your competitors include both local repair shops and online service providers.
- Local Competition: Start by identifying other auto repair shops in your area. Visit their shops, check their websites, and gather information on the services they offer and their pricing. Pay attention to the quality of their service, customer reviews, and their overall reputation in the community.
- Online Competition: With the rise of digital services, many customers turn to online platforms for repair services or parts. Identify key online competitors, such as major auto repair chains, mobile mechanics, and online parts suppliers. Analyze their service offerings, pricing, and customer satisfaction ratings.
Understanding Market Rates
Once you’ve identified your competitors, the next step is to understand the market rates for various services. This involves gathering data on what customers are paying for similar services in your area. Here are some strategies to help you gather this information:
- Surveys and Interviews: Conduct surveys or interviews with potential customers to understand what they are willing to pay for different services. This can provide valuable insights into customer expectations and price sensitivity.
- Mystery Shopping: Send someone to visit competitor shops and inquire about pricing and services. This can help you get firsthand information on how competitors are pricing their services.
- Online Research: Use online tools and resources to gather pricing information. Websites like Yelp, Google Reviews, and industry-specific forums can provide insights into what customers are paying and their satisfaction with the services received.
Positioning Your Business
Positioning your business involves determining your unique selling proposition (USP) and setting prices that reflect the value you provide. Here are some key considerations:
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Identify what sets your shop apart from the competition. This could be exceptional customer service, specialized skills, faster turnaround times, or unique services. Your USP will help you justify your pricing and attract customers who value what you offer.
- Target Market: Consider who your primary customers are. Are you targeting budget-conscious customers, premium clients looking for top-notch service, or somewhere in between? Your target market will influence your pricing strategy.
- Value Perception: Customers are willing to pay more if they perceive the value of the service to be higher. Highlight the quality of your work, the expertise of your technicians, and any guarantees or warranties you offer. Communicate the value of your services effectively to justify your prices.

Pricing Strategies
Choosing the right pricing strategy is essential for the success of your auto repair shop. The strategy you select will influence your profitability, customer satisfaction, and overall business growth. Here, we’ll explore several common pricing strategies, discuss their benefits, and provide guidance on how to implement them effectively.
Cost-Plus Pricing
Cost-plus pricing is one of the simplest and most straightforward pricing strategies. It involves calculating your total costs and adding a markup to ensure a profit.
Explanation and Benefits:
- Simplicity: This method is easy to understand and implement. You start by calculating your total costs, including both fixed and variable expenses, and then add a predetermined percentage as your profit margin.
- Cost Coverage: Ensures that all costs are covered and you make a profit on each job.
Calculation Method:
- Calculate Total Costs: Add up all your fixed and variable costs.
- Determine Desired Profit Margin: Decide on the percentage markup you want to achieve.
- Set Your Prices: Add the markup to your total costs to set your service prices.
For example, if your total cost for a repair job is $100 and you want a 20% profit margin, you would set your price at $120.
Competitive Pricing
Competitive pricing involves setting your prices based on what your competitors are charging. This strategy helps you remain competitive in the market and attract price-sensitive customers.
Explanation and Benefits:
- Market Relevance: By aligning your prices with those of your competitors, you ensure your services are competitively priced.
- Customer Attraction: This strategy can attract customers who compare prices before choosing a repair shop.
Adjusting Prices Based on Competitors:
- Monitor Competitors: Regularly check the prices of local and online competitors to stay updated on market rates.
- Adjust Accordingly: If you find your prices are significantly higher or lower than competitors, adjust them to stay competitive while ensuring profitability.
- Consider Value Additions: Sometimes, slight price differences can be justified by the additional value you offer, such as better customer service, faster turnaround times, or superior quality work.
Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing sets prices based on the perceived value of your services to the customer. If customers believe your services offer superior value, this strategy can lead to higher profit margins.
Explanation and Benefits:
- Higher Profit Margins: By pricing based on perceived value, you can often charge more than the cost-plus or competitive pricing models.
- Customer Focus: This strategy focuses on the benefits and quality you provide to customers, enhancing their perception of your service.
Setting Prices Based on Perceived Value:
- Identify Value Drivers: Determine what aspects of your service are most valuable to customers, such as expertise, speed, convenience, or quality.
- Communicate Value: Effectively market and communicate these value drivers to your customers through advertising, customer testimonials, and service descriptions.
- Price Accordingly: Set your prices based on the value you provide. For instance, if your shop offers specialized services that are rare in your area, customers may be willing to pay a premium.
Bundle Pricing
Bundle pricing involves offering packages of services at a discounted rate. This strategy can increase sales volume and provide value to customers, encouraging them to purchase more services.
Explanation and Benefits:
- Increased Sales Volume: Bundling services can encourage customers to opt for more services than they might have otherwise, increasing your overall sales.
- Perceived Value: Customers perceive they are getting a better deal by purchasing a bundle rather than individual services.
Examples of Service Bundles:
- Maintenance Packages: Offer packages that include routine maintenance services like oil changes, tire rotations, and brake inspections at a discounted rate.
- Seasonal Packages: Create bundles for seasonal needs, such as winterization packages that include tire changes, antifreeze checks, and battery inspections.
- Comprehensive Repair Packages: Combine common repairs with routine maintenance services, offering a discount compared to purchasing each service separately.
Choosing the Right Strategy
Selecting the best pricing strategy for your auto repair shop depends on various factors, including your business goals, market conditions, and customer base. Here are some tips to help you choose the right strategy:
- Analyze Your Costs: Understand your fixed, variable, and semi-variable costs to ensure your pricing covers all expenses.
- Consider Your Market: Look at what competitors are charging and what customers are willing to pay.
- Evaluate Your Value: Determine the unique value you offer and whether customers are willing to pay a premium for it.
- Test and Adjust: You may need to experiment with different pricing strategies to see what works best for your shop. Be prepared to adjust your prices based on customer feedback and market changes.

Setting Labor Rates
Labor costs are a significant part of your expenses, and setting appropriate rates ensures you cover these costs while remaining competitive. Let’s dive into the key aspects of setting labor rates effectively.
Determining Your Hourly Rate
Setting your hourly labor rate involves considering various factors to ensure your rate is competitive yet profitable. Here are the steps to determine your hourly rate:
Factors to Consider:
- Skill Level and Experience: Your technicians’ expertise and qualifications play a significant role in determining your hourly rate. Highly skilled and experienced technicians can command higher rates.
- Market Rates: Research the average hourly rates in your area. Understanding what competitors charge helps you set a rate that is competitive yet reflective of your service quality.
- Operating Costs: Consider all your costs, including fixed, variable, and semi-variable expenses. Your hourly rate must cover these costs to ensure profitability.
- Desired Profit Margin: Decide on the profit margin you aim to achieve. This margin should be factored into your hourly rate.
Formula for Calculating Hourly Rate:
- Calculate Total Monthly Costs: Sum up all your fixed, variable, and semi-variable costs for a month.
- Determine Billable Hours: Estimate the total number of hours your shop is billable in a month. Consider factors like working hours, employee productivity, and potential downtime.
- Add Desired Profit Margin: Decide on the profit margin you want to achieve and add it to your total costs.
- Set Hourly Rate: Divide the total monthly costs (including profit margin) by the billable hours to get your hourly rate.
For example, if your total monthly costs are $20,000 and you aim for a 20% profit margin, your adjusted costs would be $24,000. If your shop is billable for 1,000 hours a month, your hourly rate would be $24.
Flat Rate vs. Hourly Rate
Deciding whether to charge a flat rate or an hourly rate can impact your pricing strategy and customer satisfaction. Each approach has its advantages and disadvantages.
Pros and Cons of Flat Rate:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Predictability: Customers appreciate knowing the cost upfront, which can build trust and satisfaction. | Risk of Underestimation: If a job takes longer than expected, the flat rate may not cover the costs, affecting profitability. |
| Efficiency Incentive: Technicians are incentivized to work efficiently, as they are paid a fixed amount regardless of time taken. | Complex Jobs: For complex or unpredictable jobs, setting a flat rate can be challenging and may lead to disputes. |
| Simplified Billing: Flat rates simplify the billing process, making it easier to manage and communicate to customers. |
Pros and Cons of Hourly Rate:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Flexibility: Charging by the hour allows you to account for the actual time spent on each job, reducing the risk of undercharging. | Customer Uncertainty: Customers may be hesitant if they are unsure how long a repair will take and how much it will cost. |
| Complex Repairs: Hourly rates are better suited for complex or unpredictable jobs where the time required can vary. | Efficiency Disincentive: Technicians may not have the same incentive to work efficiently if they are paid by the hour. |
| Transparency: Customers can see a direct correlation between the time spent and the cost, which can build trust. |
➤ Read more: 10 Expert Tips & Tricks for Running a Successful Auto Repair Shop
When to Use Flat Rate vs. Hourly Rate
Choosing between a flat rate and an hourly rate depends on the type of service and customer preferences.
Flat Rate:
- Routine Services: Flat rates are ideal for routine services like oil changes, tire rotations, and brake inspections where the time required is predictable.
- Packages: Use flat rates for bundled services or maintenance packages, providing customers with clear, upfront pricing.
- Competitive Advantage: In highly competitive markets, offering flat rates can attract price-sensitive customers who prefer knowing the total cost upfront.
Hourly Rate:
- Complex Repairs: For repairs that are complex or involve diagnostic work, hourly rates are more appropriate. This ensures you are compensated for the actual time and effort spent.
- Custom Jobs: Use hourly rates for custom or specialized jobs where the time required can vary significantly.
- Customer Transparency: When customers value transparency and want to understand the breakdown of costs, hourly rates can provide that clarity.

Pricing for Parts and Materials
Accurately pricing parts and materials is crucial for maintaining profitability in your auto repair shop. This involves not only covering your costs but also ensuring that your prices are competitive and reasonable for your customers. Here, we will explore effective strategies for pricing parts and materials.
Markup Strategies
Markup is the amount added to the cost price of goods to cover overhead and profit. Different approaches can be taken when marking up parts and materials. Here’s how you can develop a markup strategy that works for your business:
Common Markup Percentages:
- Industry Standards: Typically, the markup on auto parts ranges from 25% to 100%, depending on the part and the market conditions. High-demand, fast-moving parts might have a lower markup, while specialized or hard-to-find parts can have a higher markup.
- Service Type: Routine parts like oil filters and brake pads might have a lower markup, whereas performance or custom parts can justify a higher markup.
Factors Influencing Markup Decisions:
- Part Availability: Rare or specialized parts often justify a higher markup due to their limited availability and the extra effort required to source them.
- Customer Perception: Customers are more likely to accept higher markups on parts that are integral to complex repairs or that significantly affect their vehicle’s performance and safety.
- Competition: Monitor competitors’ prices for similar parts. While you don’t need to match their prices exactly, staying within a reasonable range can help maintain competitiveness.
Sourcing Affordable Parts
The cost of parts is a significant variable expense, and sourcing affordable parts can directly impact your pricing strategy and profitability. Here are some tips on sourcing parts efficiently:
Building Relationships with Suppliers:
- Long-Term Contracts: Establishing long-term contracts with reputable suppliers can often result in better prices due to bulk purchasing and loyalty discounts.
- Preferred Supplier Lists: Develop a list of preferred suppliers who consistently offer good prices, quality parts, and reliable delivery times. This can streamline your ordering process and reduce costs.
- Negotiation: Don’t hesitate to negotiate with suppliers for better terms or bulk discounts, especially if you’re a regular buyer.
Buying in Bulk:
- Volume Discounts: Many suppliers offer significant discounts for bulk purchases. Stocking up on frequently used parts can reduce per-unit costs and improve your margins.
- Inventory Management: Efficient inventory management ensures you have the parts you need without overstocking. Use inventory software to track usage patterns and adjust your orders accordingly.
- Seasonal Purchases: Take advantage of seasonal discounts and sales to buy parts at lower prices. Planning your purchases strategically can save a substantial amount of money.
Handling Parts Margins
Managing margins on parts and materials involves balancing profitability with customer value:
Profit Margins:
- Target Margins: Set target profit margins for different categories of parts. Regularly monitor these margins to ensure you’re meeting your financial goals.
- Adjust for Market Conditions: Be flexible with your margins based on market conditions. If part costs rise, adjust your prices accordingly while maintaining transparency with your customers.
Customer Perception:
- Value for Money: Ensure customers perceive they are getting good value for their money. This involves not only fair pricing but also quality service and transparent communication.
- Customer Education: Educate customers on why certain parts might cost more. For example, explaining the benefits of OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts versus aftermarket parts can help justify higher prices.
Pricing Transparency
Transparency in pricing parts and materials builds trust with your customers. Here’s how to approach this:
Itemized Estimates:
- Detailed Quotes: Provide customers with itemized estimates that break down the cost of parts, labor, and any other charges. This helps customers understand exactly what they’re paying for.
- Explain Markups: Be prepared to explain your markup strategy to customers if asked. Transparency about how you price parts can enhance customer trust and satisfaction.
Competitive Pricing:
- Regular Reviews: Review your parts pricing regularly to ensure it remains competitive while covering your costs. Adjust prices based on changes in supplier costs, market conditions, and competitor pricing.
- Price Matching: If feasible, consider offering a price-matching policy for parts. This can reassure customers that they are getting a fair deal without having to shop around.
Warranty and Quality Assurance
Offering warranties and quality assurance on parts can justify higher prices and enhance customer satisfaction:
Part Warranties:
- Manufacturer Warranties: Use parts that come with manufacturer warranties and clearly communicate these to your customers. This adds value and peace of mind.
- Shop Warranties: Consider offering your own warranty on parts and labor. This can differentiate your shop from competitors and justify a higher markup.
Quality Assurance:
- Reliable Suppliers: Ensure you source parts from reliable suppliers known for quality. Using subpar parts can lead to failures and damage your reputation.
- Quality Checks: Implement a quality assurance process for all incoming parts to verify their condition and compatibility before use.

Special Offers and Discounts
Special offers and discounts are powerful tools for attracting new customers, retaining existing ones, and boosting sales. However, they need to be carefully planned to ensure they don’t erode your profit margins. Here’s how to effectively implement special offers and discounts in your auto repair shop.
Types of Discounts
There are several types of discounts you can offer, each with its own benefits and ideal use cases. Here are some common types:
Volume Discounts:
- Explanation: Offer discounts to customers who purchase multiple services or parts. For example, you could provide a discount on the total bill if a customer gets an oil change, tire rotation, and brake inspection in one visit.
- Benefits: Encourages customers to bundle services, increasing your overall sales volume and efficiency.
Loyalty Discounts:
- Explanation: Reward repeat customers with discounts or special offers. This can be done through a loyalty program where customers earn points for each visit that can be redeemed for discounts or free services.
- Benefits: Builds long-term customer relationships and encourages repeat business, increasing customer lifetime value.
Seasonal Promotions:
- Explanation: Offer discounts during specific times of the year, such as back-to-school, winter preparation, or summer road trip readiness. These promotions can be tied to seasonal maintenance needs.
- Benefits: Helps smooth out demand fluctuations and brings in business during slower periods.
Referral Discounts:
- Explanation: Provide discounts to customers who refer new clients to your shop. Both the referrer and the new customer can receive a discount on their next service.
- Benefits: Leverages word-of-mouth marketing, bringing in new customers at a low acquisition cost.
Impact on Profitability
While discounts can drive sales and customer retention, they can also impact your profitability. Here’s how to balance the benefits and risks:
Balancing Discounts with Profit Margins:
- Calculate Costs: Before offering any discount, calculate the impact on your profit margins. Ensure that even with the discount, your prices cover costs and contribute to your desired profit margin.
- Set Limits: Establish limits on discounts to prevent excessive price cuts. For example, cap the maximum discount a customer can receive, or limit the number of discounted services per month.
Targeted Offers:
- Customer Segmentation: Use customer data to create targeted offers. For instance, offer loyalty discounts to long-term customers or seasonal promotions to customers who have previously taken advantage of similar offers.
- Monitor Results: Track the effectiveness of your discounts. Analyze data on sales volume, customer acquisition, and profitability to understand which discounts work best and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Implementing a Discount Strategy
A well-planned discount strategy can boost your shop’s performance without compromising profitability. Here’s how to implement an effective discount strategy:
Guidelines for Offering Discounts:
- Clear Objectives: Define the goals of your discount program. Are you aiming to attract new customers, increase repeat business, or boost sales during slow periods? Clear objectives will guide your discount strategy.
- Promotion: Effectively promote your discounts through various channels, such as social media, email newsletters, and in-shop signage. Clear communication ensures customers are aware of your offers.
- Staff Training: Train your staff to explain and apply discounts correctly. Ensure they understand the terms of each discount and can communicate the value to customers.
Creating a Sense of Urgency:
- Limited-Time Offers: Use limited-time discounts to create urgency. For example, a “10% off all services this weekend only” can drive immediate traffic to your shop.
- Exclusive Deals: Offer exclusive deals to your loyal customers or email subscribers. Making customers feel special can increase engagement and loyalty.
Customer Feedback:
- Gather Insights: Solicit feedback from customers about your discount programs. Understand what they find appealing and what could be improved.
- Adjust Offers: Use customer feedback to refine your discount strategy. If a particular discount isn’t resonating, consider modifying it or trying a different approach.
Monitoring and Measuring Success
To ensure your discount strategy is effective, it’s crucial to monitor and measure its success:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Sales Volume: Track changes in sales volume during discount periods compared to regular times.
- Customer Acquisition: Measure the number of new customers attracted by the discounts.
- Customer Retention: Evaluate the impact of discounts on customer retention rates and repeat business.
- Profit Margins: Analyze how discounts affect your overall profit margins. Ensure that increased sales volume compensates for the reduced price per service.
Adjusting Based on Results:
- Data Analysis: Regularly review data and performance metrics to assess the effectiveness of your discount strategy.
- Flexibility: Be prepared to adjust your strategy based on what the data shows. If certain discounts aren’t driving the desired results, modify or replace them with new offers.
Indeed, when implemented strategically, special offers and discounts can significantly boost your auto repair shop’s sales and customer loyalty. Use these tools to grow your business while maintaining healthy profit margins.

Maximizing Profitability
Maximizing profitability in your auto repair shop goes beyond setting the right prices. It involves strategic actions that improve revenue and reduce costs. Here’s how to maximize your shop’s profitability through upselling, cross-selling, efficient operations, and customer retention.
Upselling and Cross-Selling
Upselling and cross-selling are effective strategies to increase the average transaction value by offering additional services or products that complement the customer’s initial purchase.
Techniques for Upselling and Cross-Selling:
- Service Packages: Create service packages that combine multiple related services at a discounted rate. For example, offer a package that includes an oil change, tire rotation, and brake inspection.
- Recommend Upgrades: Suggest upgrades or additional services that enhance the customer’s vehicle performance or safety. For instance, recommend premium oil during an oil change or suggest a tire upgrade for better traction.
- Highlight Benefits: Clearly explain the benefits of the additional services or products. Customers are more likely to agree to an upsell or cross-sell if they understand how it will improve their vehicle’s performance or longevity.
Training Staff to Effectively Upsell:
- Product Knowledge: Ensure your staff has a thorough knowledge of all the services and products you offer. They should be able to confidently explain the benefits and features to customers.
- Customer Interaction: Train your staff on how to approach customers with upsell and cross-sell suggestions without being pushy. Focus on customer needs and how the additional services can meet those needs.
- Incentives: Offer incentives to your staff for successful upselling and cross-selling. This can motivate them to actively promote additional services and products.
Efficient Operations
Streamlining your shop’s operations can significantly reduce costs and increase profitability. Efficient operations ensure that you make the most of your resources and minimize waste.
Streamlining Processes to Reduce Costs:
- Workflow Optimization: Analyze your current workflow and identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies. Implement changes to streamline processes, such as organizing tools and parts for easy access or rearranging the shop layout for better workflow.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop SOPs for common tasks to ensure consistency and efficiency. Train your staff to follow these procedures to reduce errors and save time.
- Technology and Tools: Invest in technology and tools that enhance productivity. This can include diagnostic equipment, inventory management software, and customer relationship management (CRM) systems.
Inventory Management:
- Just-in-Time Inventory: Adopt a just-in-time inventory system to reduce the amount of stock you hold and minimize storage costs. Order parts as needed based on upcoming jobs and demand forecasts.
- Supplier Relationships: Build strong relationships with reliable suppliers to ensure timely delivery of parts and materials. Negotiate better terms and prices to reduce costs.
- Inventory Tracking: Use inventory management software to track parts and materials. This helps prevent overstocking or stockouts and ensures you have the right parts when needed.
Customer Retention
Retaining existing customers is often more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. Loyal customers not only provide repeat business but also refer others to your shop.
Importance of Repeat Business:
- Consistent Revenue: Loyal customers provide a steady stream of revenue, which is crucial for maintaining cash flow and profitability.
- Cost Savings: It’s typically less expensive to retain a customer than to attract a new one, as you save on marketing and acquisition costs.
Strategies to Retain Customers:
- Exceptional Service: Provide exceptional customer service to ensure customers have a positive experience. This includes friendly interactions, timely service, and high-quality repairs.
- Follow-Up: Implement follow-up procedures to check in with customers after their service. This can include phone calls, emails, or surveys to ensure satisfaction and address any issues.
- Loyalty Programs: Develop a loyalty program that rewards repeat customers with discounts, free services, or special offers. This incentivizes customers to return to your shop for future needs.
Building Customer Relationships:
- Personalization: Personalize your interactions with customers by remembering their names, preferences, and service history. This creates a more personal connection and enhances customer loyalty.
- Communication: Maintain regular communication with your customers through newsletters, social media, and special promotions. Keep them informed about new services, offers, and important maintenance tips.
- Feedback Mechanism: Encourage customers to provide feedback and actively use it to improve your services. Address any complaints promptly and show customers that their opinions are valued.
Thus, by effectively upselling and cross-selling, streamlining operations, and prioritizing customer retention, you can make your shop even more profitable and ensure long-term success.
➤ Read more: Maximizing Downtime in Your Auto Repair Shop
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How can I make my auto repair business more profitable?
Maximize profitability by focusing on key strategies such as upselling and cross-selling services, streamlining operations for better efficiency, implementing customer retention programs, and regularly reviewing and adjusting prices. Additionally, invest in staff training, optimize inventory management, and expand marketing efforts to attract new customers. By balancing these approaches, you can boost revenue, reduce costs, and maintain a competitive edge in the market while ensuring customer satisfaction.
Q: How do I determine the best pricing strategy for my auto repair shop?
To determine the best pricing strategy for your auto repair shop, analyze your costs, market competition, and target customers. Consider a mix of cost-plus pricing for parts and value-based pricing for labor. Research local competitors’ rates and adjust accordingly. Factor in your shop’s unique selling points, such as expertise or specialized services. Regularly review and adjust prices to maintain profitability while staying competitive. Test different pricing models and monitor their impact on customer retention and overall revenue. Remember, the ideal strategy balances fair pricing for customers with sustainable profits for your business.
Q: What are the common costs in an auto repair business?
Common costs in auto repair businesses include fixed costs (rent, utilities, insurance, base salaries), variable costs (parts, direct labor, supplies), and semi-variable costs (overtime pay, tiered utilities). Other expenses may include equipment maintenance, marketing, and software subscriptions. These costs can vary depending on the shop’s size, location, and specialization but are essential to consider when budgeting and pricing services.
Q: What financial metrics should I track in my auto repair business?
Key financial metrics to track in an auto repair business include gross profit margin, net profit margin, labor efficiency ratio, average repair order value, customer retention rate, and parts inventory turnover. Additionally, monitor cash flow, accounts receivable aging, and operating expenses as a percentage of revenue. Regularly analyzing these metrics helps identify trends, pinpoint areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to enhance profitability and overall business performance.
Q: How do you price labor competitively and still make money?
To price labor competitively while maintaining profitability, start by accurately calculating your shop’s hourly operating costs. Research local market rates and set your labor prices slightly above average if you offer superior service or expertise. Use flat-rate pricing for common repairs to improve efficiency. Regularly review and adjust your rates based on changes in costs and market conditions. Balance competitive pricing with the value you provide, ensuring your rates cover expenses and generate a reasonable profit margin.
Q: How can I cut operating costs in my auto repair business?
To cut operating costs in your auto repair business, focus on optimizing efficiency in all areas. Streamline workflow processes, invest in energy-efficient equipment, negotiate better rates with suppliers, and implement inventory management systems to reduce waste. Cross-train employees to handle multiple tasks, minimize overtime and consider outsourcing non-core functions. Regularly review and adjust your pricing strategy to ensure profitability. Embrace technology for improved diagnostics and customer communication, potentially reducing time spent on each job while improving service quality.
Q: How can I make my auto repair business run more efficiently?
To improve efficiency in your auto repair business, implement a streamlined workflow process, invest in modern diagnostic tools and equipment, and utilize management software for scheduling and inventory control. Train staff in multiple areas to increase flexibility, and organize the workspace for optimal productivity. Regularly maintain equipment to prevent downtime. Improve communication with customers to reduce delays and misunderstandings. Consider offering pick-up and delivery services to maximize bay usage. Regularly review and optimize processes based on performance data and employee feedback.
Last Words
Of course, when it comes to setting up pricing strategies and profitability, there are plenty of things to consider. But while it seems daunting, you can always set yourself up for success with the right strategies and a clear understanding of your costs and market.
More than just numbers, pricing is also about the value you provide and the trust you build with your customers. As you fine-tune your pricing strategies, keep the lines of communication open with your clients and stay adaptable to changes in the market.
Trust me, your dedication to fairness and quality service will always show. It’s going to drive profitability and foster lasting customer relationships.
I hope you’ve learned a thing or two about how to set up pricing strategies and profitability for your auto shop. Here’s to steering your business towards a prosperous and rewarding future!








