OBD-II Code P0125 is an important diagnostic trouble code that indicates a malfunction in a vehicle’s cooling system affecting its emissions control and fuel efficiency.
What Does the P0125 Code Mean?
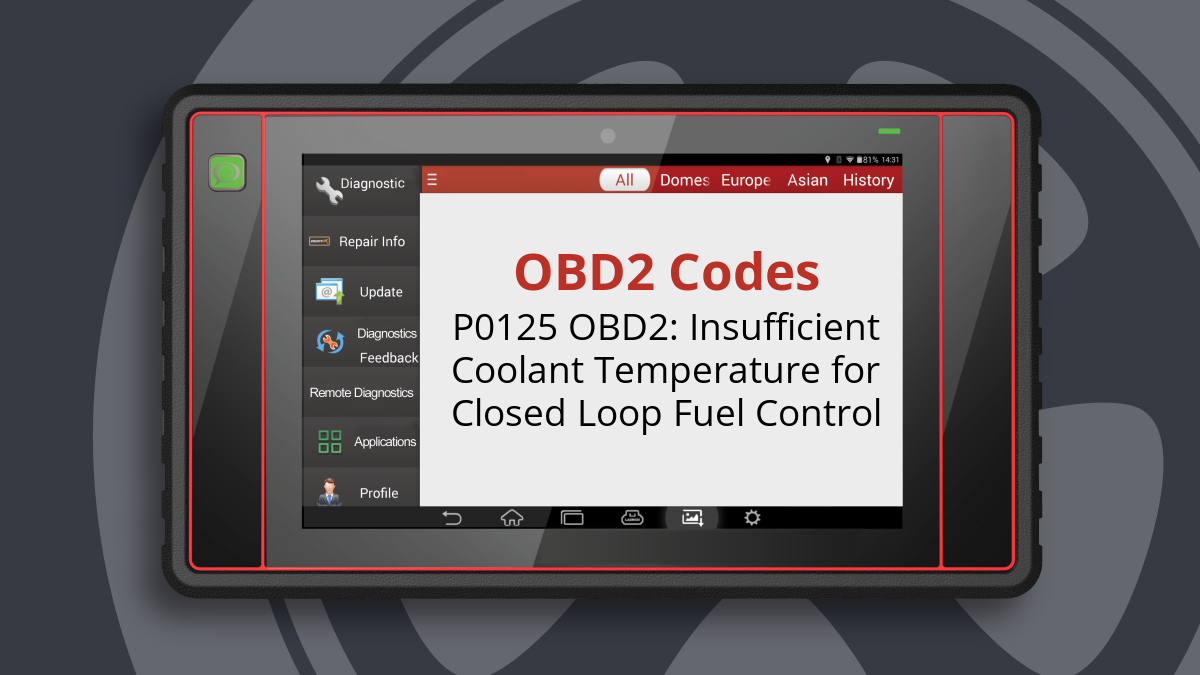
The P0125 code stands for “Insufficient Coolant Temperature For Closed Loop Fuel Control.” This code indicates that the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) has detected that the engine coolant temperature is not reaching the necessary level for optimal fuel and ignition control. Specifically, the engine should reach a coolant temperature of 160-170 degrees Fahrenheit within 15 minutes of a cold start.
What Causes the P0125 Code?
Several factors can lead to a P0125 code, including:
- Defective engine thermostat
- Faulty engine coolant temperature sensor
- Defective intake air temperature sensor
- Cooling system issues
- Low engine coolant levels
- Dirty engine coolant affecting sensor readings
- Defective cooling fan that runs continuously
What Are the Symptoms of the P0125 Code?
The symptoms associated with the P0125 code include:
- Check Engine Light illuminated
- Vehicle may not shift into the highest gear at freeway speeds
- Decreased fuel economy
- In some cases, no noticeable symptoms may be detected by the driver
How Serious Is the P0125 Code?
The P0125 code is considered urgent. It indicates a significant malfunction that can lead to increased emissions and potential damage to the engine if not addressed promptly. Ignoring this code may also lead to poor fuel economy and can impact the vehicle’s overall performance.
How to Diagnose the P0125 Code
To diagnose the P0125 code effectively, follow these steps:
- Record freeze frame data to understand the vehicle’s operating conditions when the code was set, paying close attention to MPH, TPS, LOAD, RPM, and coolant temperature.
- Connect a scanner to monitor the engine sensor data and start the vehicle with the heater off.
- Observe the coolant temperature readings. If they do not reach 160-170 degrees Fahrenheit within fifteen minutes, the thermostat is likely the issue.
- Use a laser pyrometer to verify the coolant temperature readings against actual engine temperature to rule out sensor issues.
- Check that the cooling fan is not continuously running, which could prevent the engine from reaching normal operating temperatures.
- Ensure the intake air temperature sensor readings are reasonable compared to the outside air and under-hood temperatures.
Common Repairs for the P0125 Code
Common repairs associated with the P0125 code may include:
- Replacing a faulty engine thermostat
- Replacing the engine coolant temperature sensor
- Addressing cooling system leaks
- Flushing and replacing dirty engine coolant
- Repairing or replacing defective cooling fans
How Much Does It Cost to Fix the P0125 Code?
The repair cost for a P0125 code can vary widely depending on the specific issue. Typical costs may range from $100 to $500, depending on whether parts need to be replaced or if the problem lies within the cooling system itself. Always consult with a qualified mechanic for an accurate estimate.
Can I Fix the P0125 Code Myself?
While some individuals with automotive knowledge may attempt to fix the P0125 code themselves, it is recommended to consult with a professional mechanic. Proper diagnosis and repair require specialized tools and experience to avoid misdiagnosing the issue, which could lead to further complications.