
Scania DSC9 DSC 9 Engine Workshop Manual
What's Included?
Fast Download Speeds
Online & Offline Access
Access PDF Contents & Bookmarks
Full Search Facility
Print one or all pages of your manual

DSC 9 Engine Workshop
SCANIA Manual
This manual covers the following engines up to 1996
3 Series Trucks
DSC 9 10 (220Hp)
DSC 9 07 (250Hp)
DSC 9 09 (250Hp)
DSC 9 08 (280Hp)
4 Series Trucks
DSC 9 11 (220Hp)
DSC 9 12 (260Hp)
DSC 9 13 (310Hp)
Manual Contents:
Description of Operation .....
Engine Overhaul Description
C M0
from the library of Barrington Diesel Club
2
18
SCANIA
service
Contents
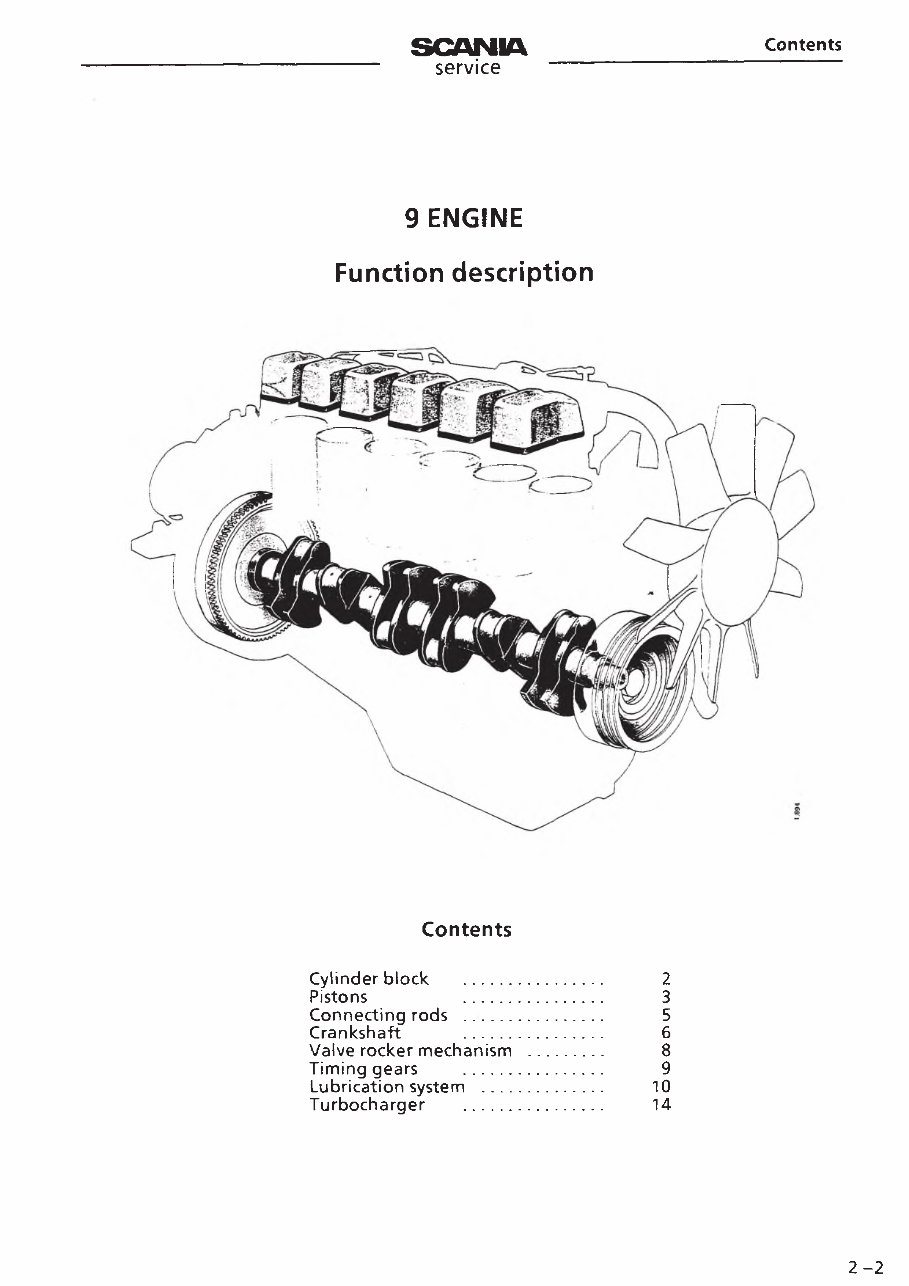
9 ENGINE
Function description
Contents
Cylinder block ...................................... 2
Pistons 3
Connecting rods ................................. 5
Crankshaft 6
Valve rocker mechanism ..................... 8
Timing gears ...................................... 9
Lubrication system ................................. 10
Turbocharger ...................................... 14
2-2
from the library of Barrington Diesel Club
Cylinder block
SCANIA
service
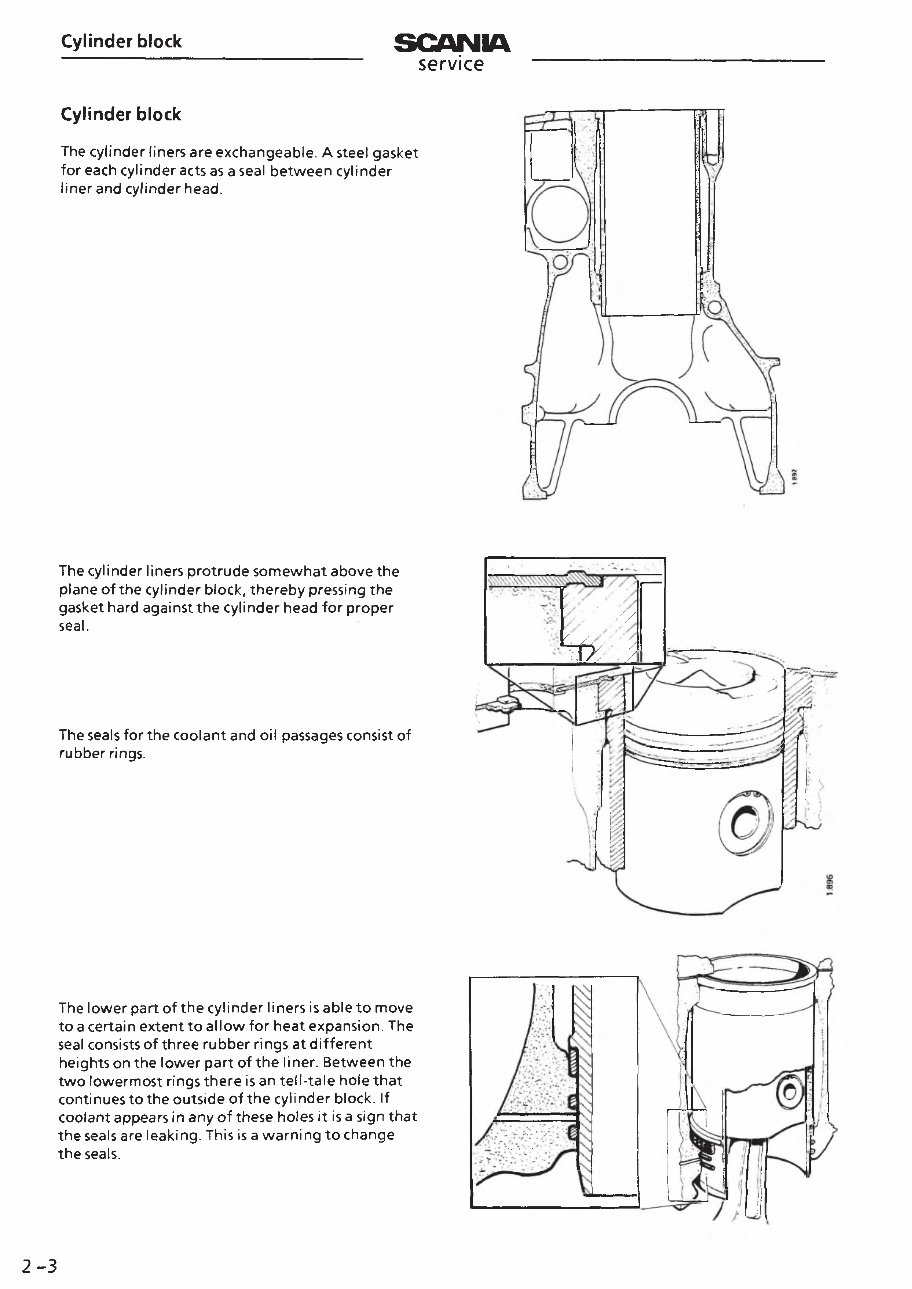
Cylinder block
The cylinder liners are exchangeable. A steel gasket
for each cylinder acts as a seal between cylinder
liner and cylinder head.
The cylinder liners protrude somewhat above the
plane of the cylinder block, thereby pressing the
gasket hard against the cylinder head for proper
seal.
The seals for the coolant and oil passages consist of
rubber rings.
'' •//
H y /./,
The lower part of the cylinder liners is able to move
to a certain extent to allow for heat expansion. The
seal consists of three rubber rings atdifferent
heights on the lower part of the liner. Between the
two lowermost rings there is an tell-tale hole that
continues to the outside of the cylinder block. If
coolant appears in any of these holes it is a sign that
the seals are leaking. This is a warning to change
the seals.
2-3
from the library of Barrington Diesel Club
SCANIA
service
Pistons
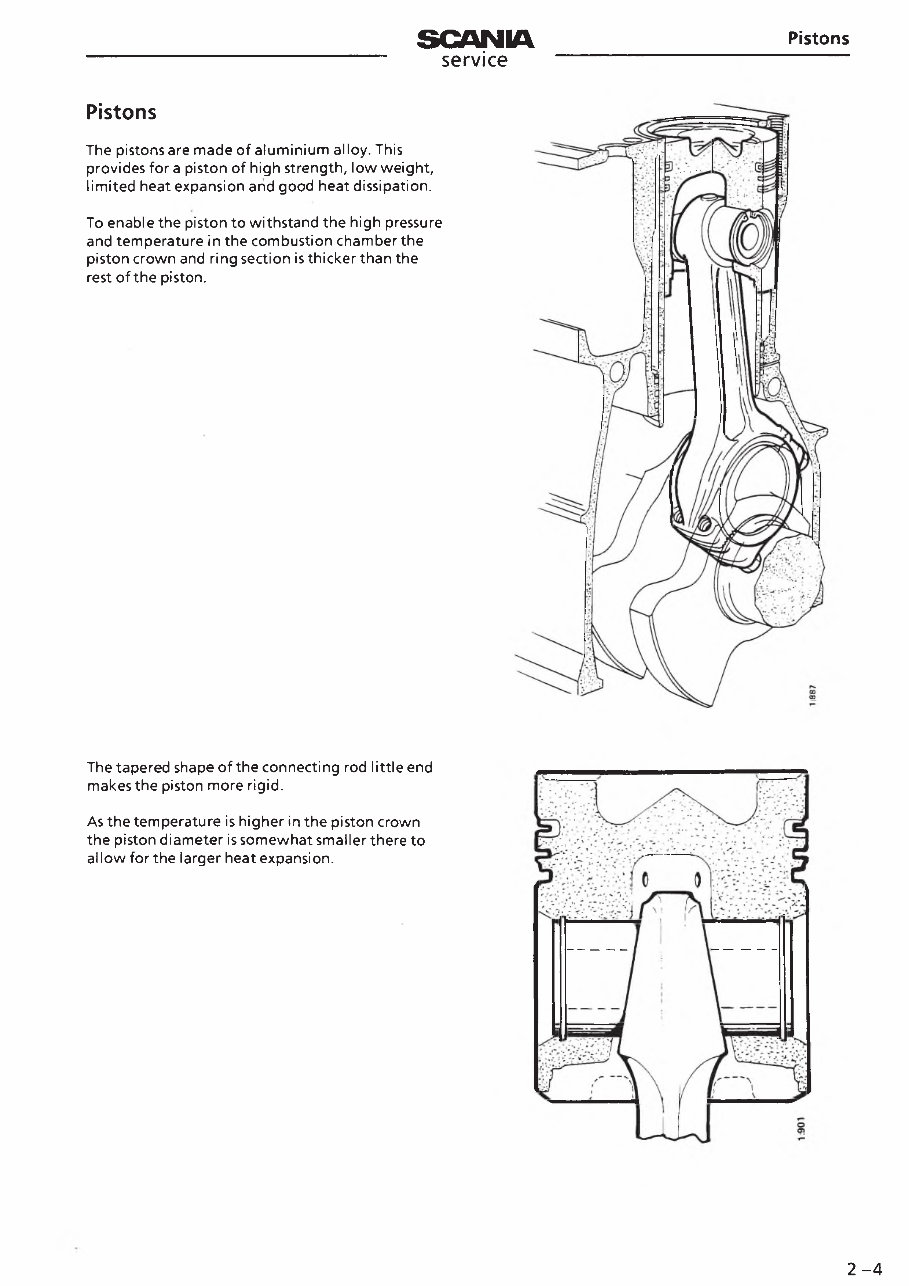
Pistons
The pistonsare made of aluminium alloy. This
provides for a piston of high strength, low weight,
limited heat expansion and good heat dissipation.
To enable the piston to withstand the high pressure
and temperature in the combustion chamber the
piston crown and ring section is thicker than the
rest of the piston.
The tapered shape of the connecting rod little end
makes the piston more rigid.
As the temperature is higher in the piston crown
the piston diameter is somewhat smaller there to
allow for the larger heat expansion.
2-4
from the library of Barrington Diesel Club
Pistons
SCANIA
service
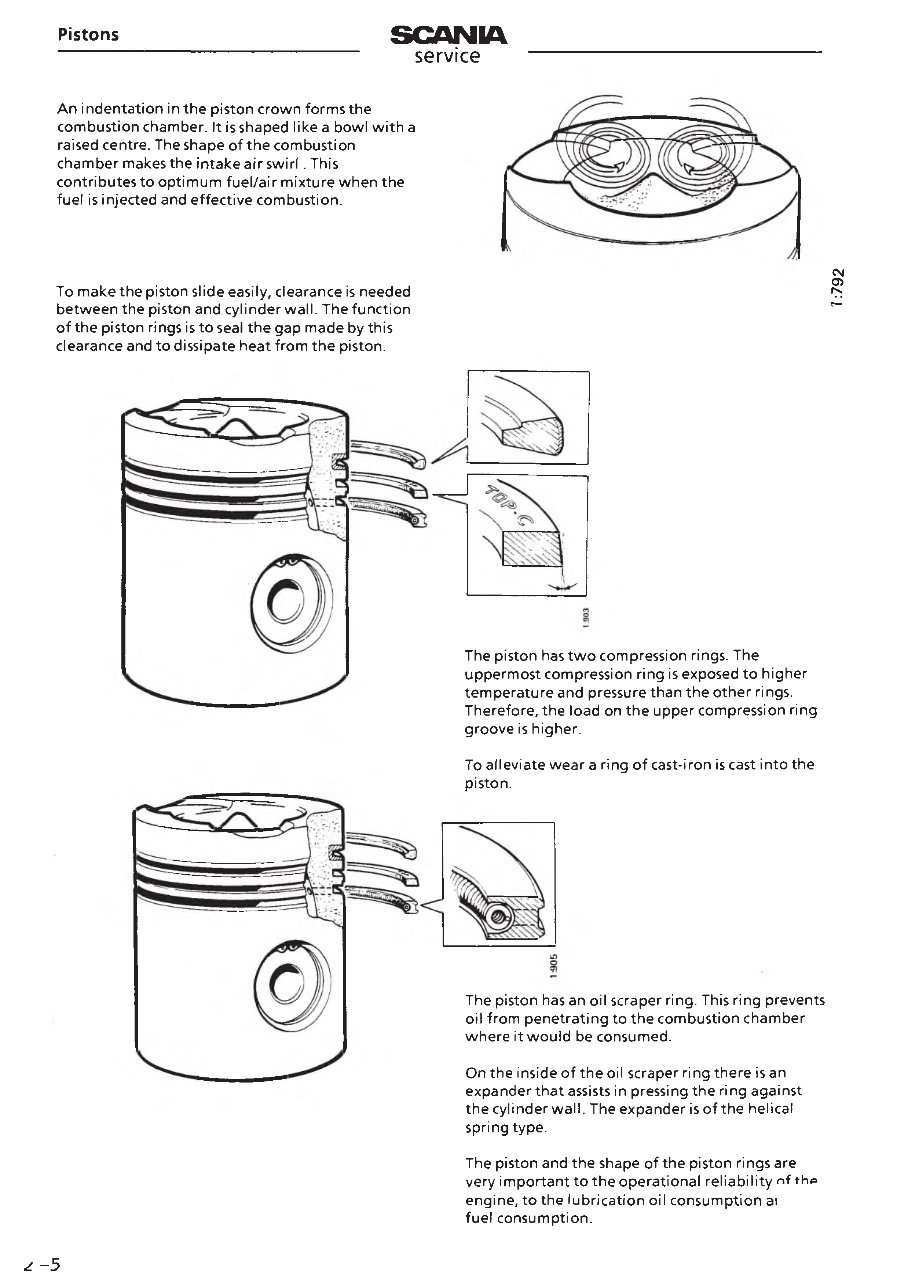
An indentation inthe piston crown forms the
combustion chamber. It is shaped like a bowl with a
raised centre. The shape of the combustion
chamber makes the intake air sw irl. This
contributes to optimum fuel/air mixture when the
fuel is injected and effective combustion.
To make the piston slide easily, clearance is needed
between the piston and cylinder wall. The function
of the piston rings is to seal the gap made by this
clearance and to dissipate heat from the piston.
The piston has two compression rings. The
uppermost compression ring is exposed to higher
temperature and pressure than the other rings.
Therefore, the load on the upper compression ring
groove is higher.
To alleviate wear a ring of cast-iron is cast into the
piston.
The piston has an oil scraper ring. This ring prevents
oil from penetrating to the combustion chamber
where it would be consumed.
On the inside of the oil scraper ring there is an
expanderthat assists in pressing the ring against
the cylinder wall. The expander is of the helical
spring type.
The piston and the shape of the piston rings are
very important to the operational reliability of the
engine, to the lubrication oil consumption and the
fuel consumption.
^ -5
1:792
from the library of Barrington Diesel Club
SCANIA
service
Connecting rods
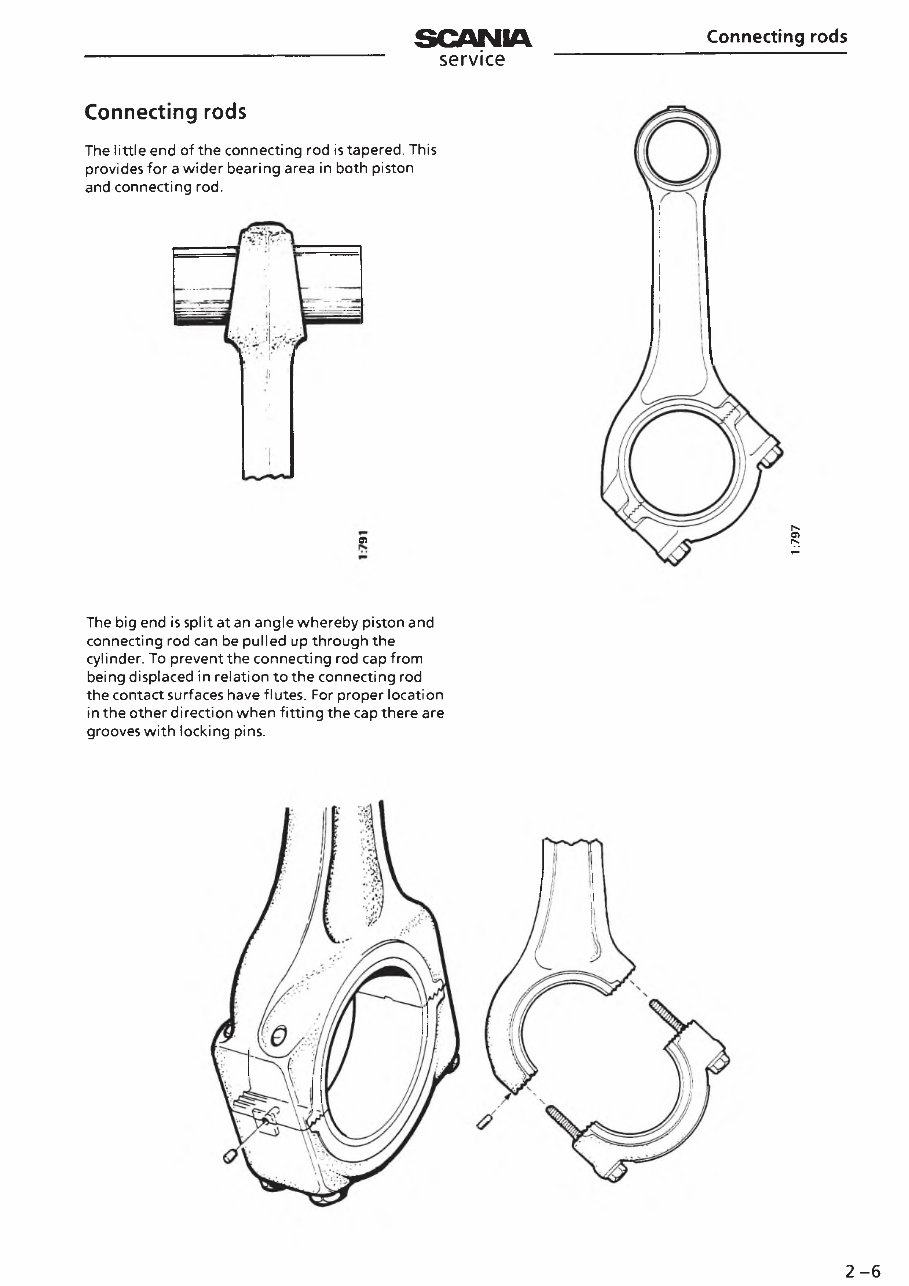
Connecting rods
The little end of the connecting rod is tapered. This
provides for a wider bearing area in both piston
and connecting rod.
0)
The big end is split at an angle whereby piston and
connecting rod can be pulled up through the
cylinder. To prevent the connecting rod cap from
being displaced in relation to the connecting rod
the contact surfaces have flutes. For proper location
in the other direction when fitting the cap there are
grooves with locking pins.
2-6
1:797
from the library of Barrington Diesel Club
Crankshaft
SCANIA
service
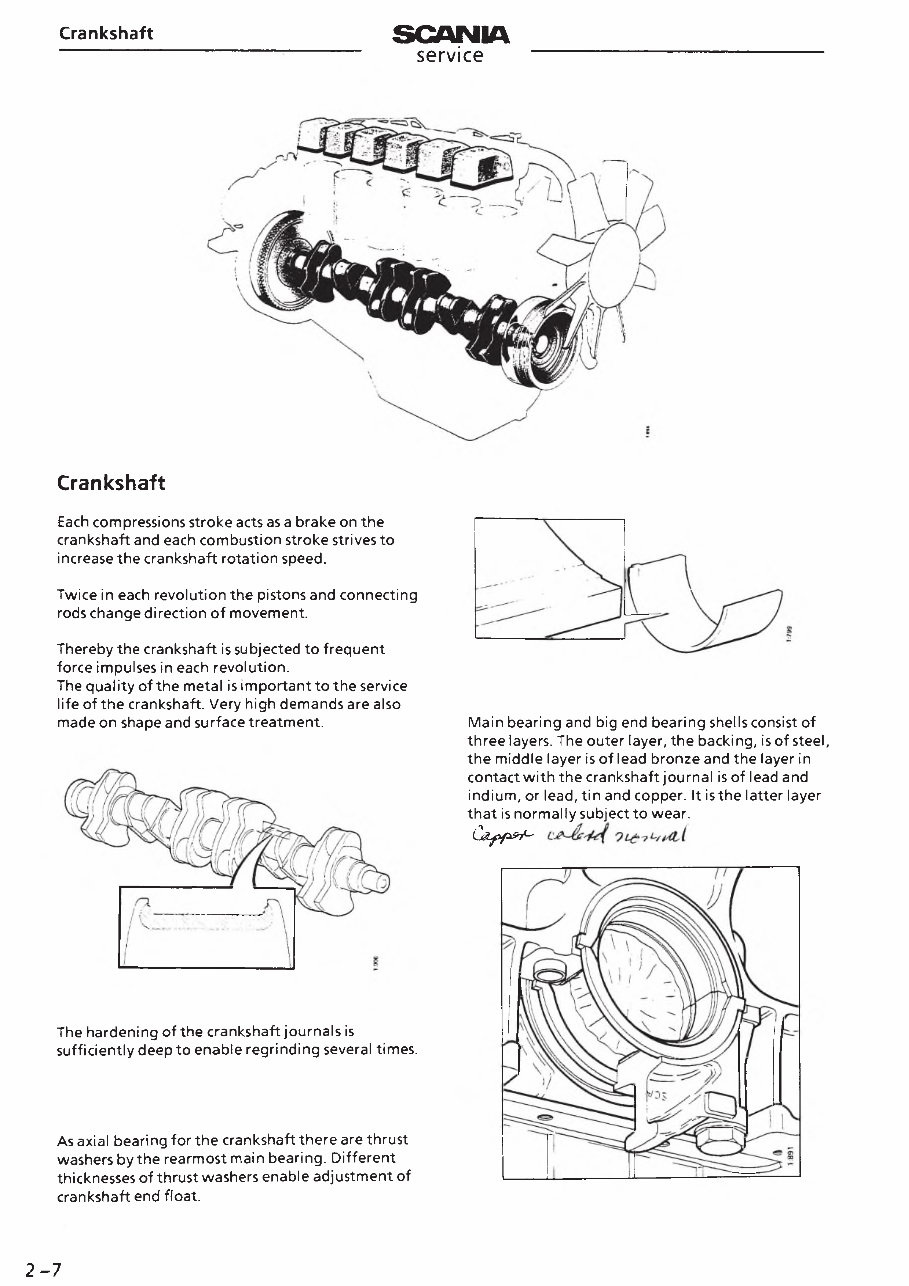
Crankshaft
Each compressions stroke acts as a brake on the
crankshaft and each combustion stroke strives to
increase the crankshaft rotation speed.
Twice in each revolution the pistons and connecting
rods change direction of movement.
Thereby the crankshaft is subjected to frequent
force impulses in each revolution.
The quality of the metal is important to the service
life of the crankshaft. Very high demands are also
made on shape and surface treatment.
The hardening of the crankshaft journals is
sufficiently deep to enable regrinding several times.
As axial bearing for the crankshaft there are thrust
washers by the rearmost main bearing. Different
thicknesses of thrust washers enable adjustment of
crankshaft end float.
Main bearing and big end bearing shells consist of
three layers. The outer layer, the backing, is of steel,
the middle layer is of lead bronze and the layer in
contact with the crankshaft journal is of lead and
indium, or lead, tin and copper. It isthe latter layer
that is normally subject to wear.
CjjLpf&i-'
2-7
from the library of Barrington Diesel Club
SCANIA
service
Crankshaft
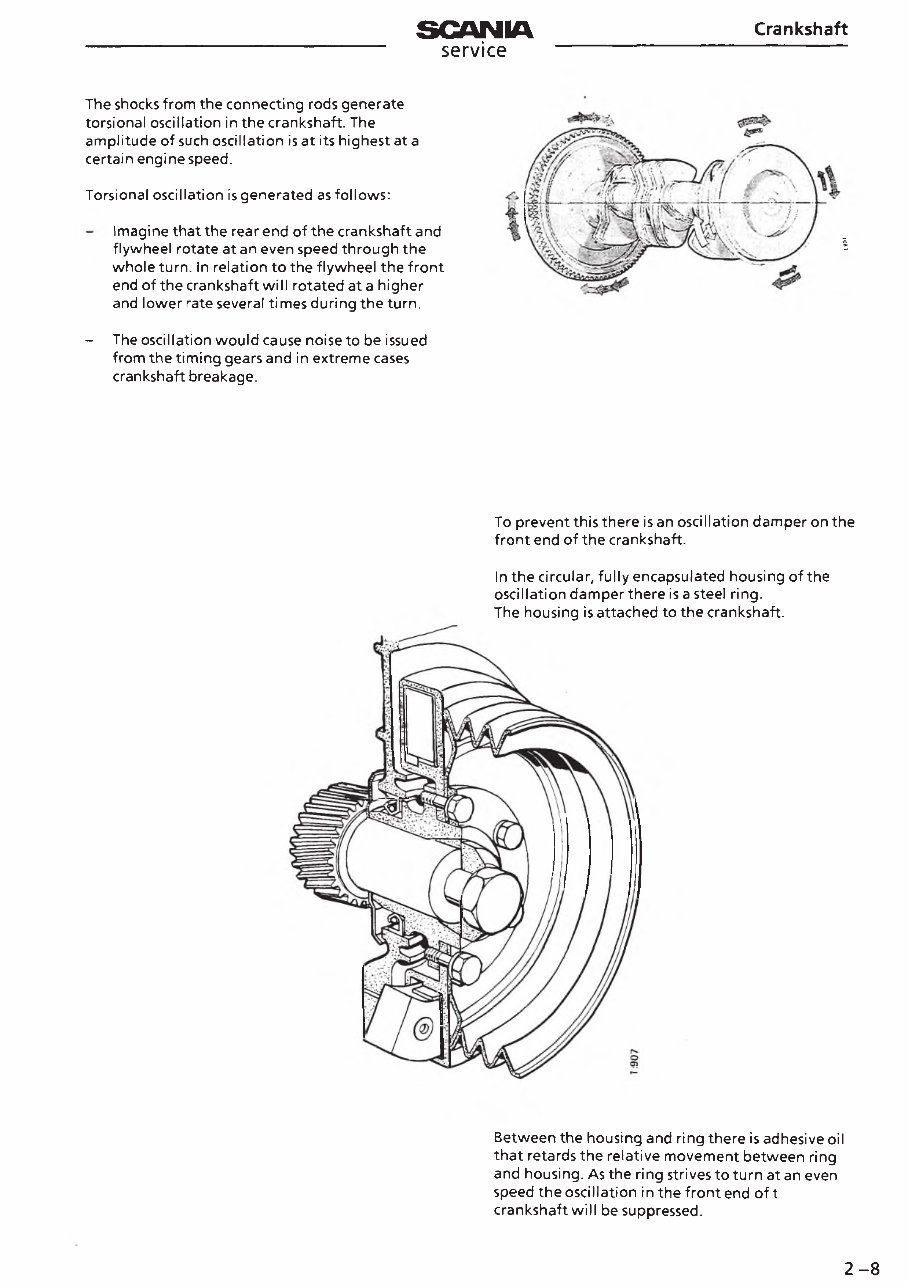
The shocks from the connecting rods generate
torsional oscillation in the crankshaft. The
amplitude of such oscillation is at its highest at a
certain engine speed.
Torsional oscillation is generated as follows:
Imagine that the rear end of the crankshaft and
flywheel rotate at an even speed through the
whole turn. In relation to the flywheel the front
end of the crankshaft will rotated at a higher
and lower rate several times during the turn.
- The oscillation would cause noise to be issued
from the timing gears and in extreme cases
crankshaft breakage.
To prevent this there is an oscillation damper on the
front end of the crankshaft.
In the circular, fully encapsulated housing of the
oscillation damper there is a steel ring.
The housing is attached to the crankshaft.
Between the housing and ring there is adhesive oil
that retards the relative movement between ring
and housing. As the ring strives to turn at an even
speed the oscillation in the front end of the
crankshaft will be suppressed.
2-8
t.«ol
from the library of Barrington Diesel Club
Valve rocker mechanism
SCANIA
service
Valve rocker mechanism
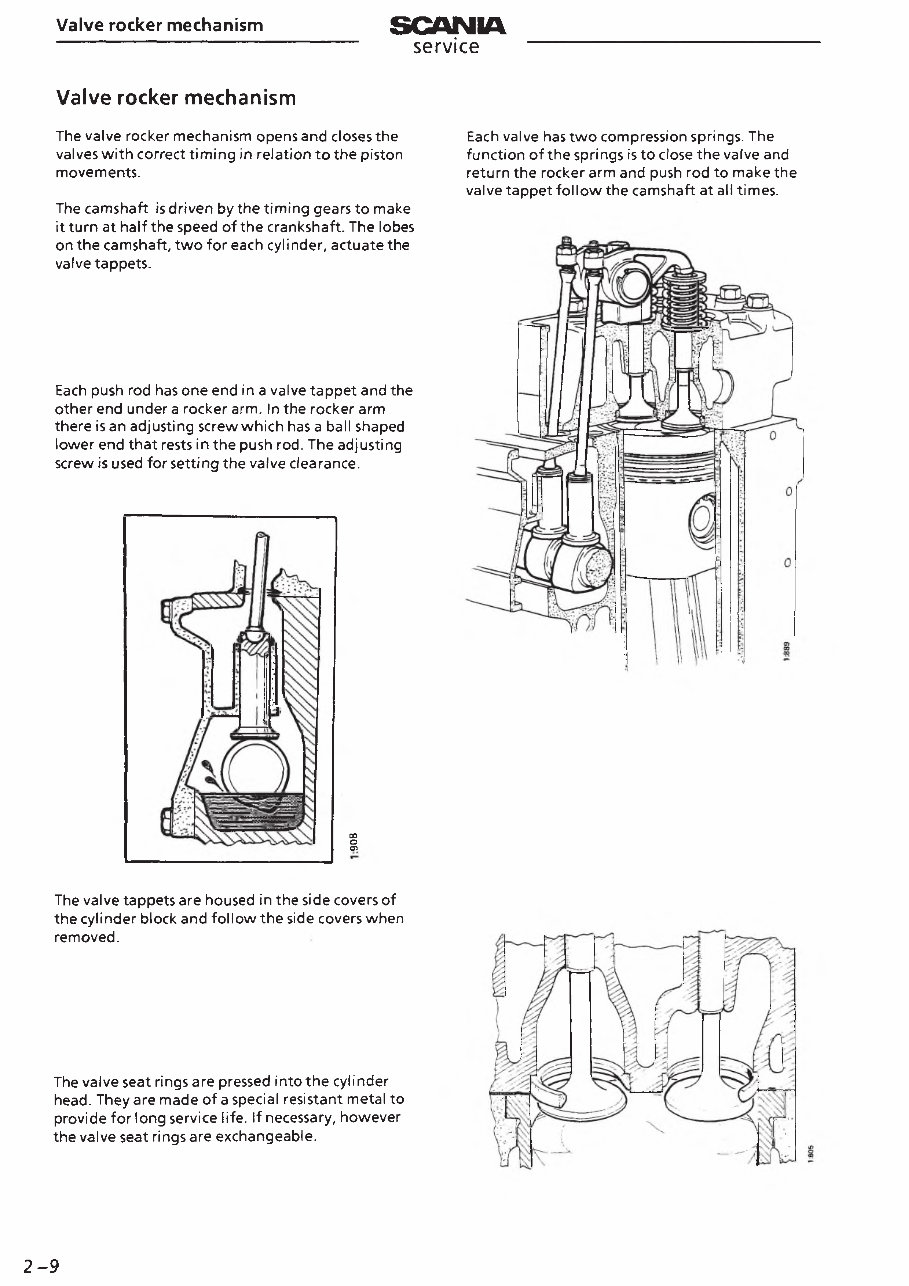
The valve rocker mechanism opens and closes the
valves with correct timing in relation to the piston
movements.
The camshaft is driven by the timing gears to make
it turn at half the speed of the crankshaft. The lobes
on the camshaft, two for each cylinder, actuate the
valve tappets.
Each push rod has one end in a valve tappet and the
other end under a rocker arm. In the rocker arm
there is an adjusting screw which has a ball shaped
lower end that rests in the push rod. The adjusting
screw is used for setting the valve clearance.
Each valve has two compression springs. The
function of the springs is to close the valve and
return the rocker arm and push rod to make the
valve tappet follow the camshaft at all times.
00
O
CT>
The valve tappets are housed in the side covers of
the cylinder block and follow the side covers when
removed.
The valve seat rings are pressed into the cylinder
head. They are made of a special resistant metal to
provide for long service life. If necessary, however
the valve seat rings are exchangeable.
2-9
from the library of Barrington Diesel Club
SCANIA
service
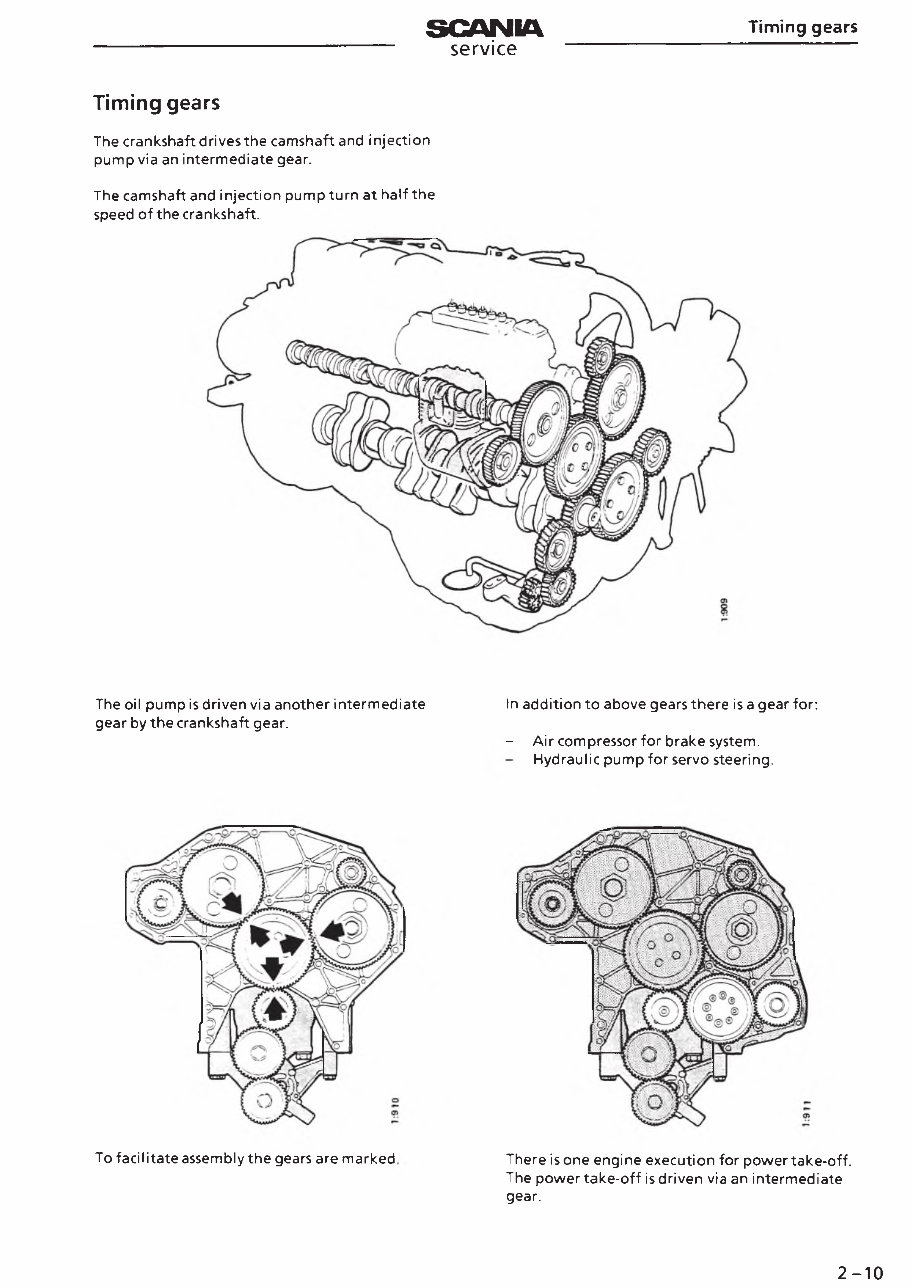
Timing gears
Timing gears
The crankshaft drives the camshaft and injection
pump via an intermediate gear.
The camshaft and injection pump turn at half the
speed of the crankshaft.
The oil pump is driven via another intermediate
gear by the crankshaft gear.
In addition to above gears there is a gear for:
- Air compressor for brake system.
Hydraulic pump for servo steering.
To facilitate assembly the gears are marked
There is one engine execution for power take-off.
The power take-off is driven via an intermediate
gear.
2-10
from the library of Barrington Diesel Club
You're Reading a Preview
What's Included?
Fast Download Speeds
Online & Offline Access
Access PDF Contents & Bookmarks
Full Search Facility
Print one or all pages of your manual
$41.99
$54.99
Viewed 99 Times Today


Loading...
Secure transaction
What's Included?
Fast Download Speeds
Online & Offline Access
Access PDF Contents & Bookmarks
Full Search Facility
Print one or all pages of your manual
$41.99
$54.99
DSC 9 Engine Workshop Manual
This manual provides comprehensive coverage for the following engines up to 1996:
- 3 Series Trucks: DSC 9 10 (220Hp), DSC 9 07 (250Hp), DSC 9 09 (250Hp), DSC 9 08 (280Hp)
- 4 Series Trucks: DSC 9 11 (220Hp), DSC 9 12 (260Hp), DSC 9 13 (310Hp)
Manual Contents:
- Description of Operation
- Engine Overhaul Description




