
Panasonic DMR-EZ48V EZ48VEB Service Manual and Repair Guide
What's Included?
Fast Download Speeds
Online & Offline Access
Access PDF Contents & Bookmarks
Full Search Facility
Print one or all pages of your manual

© 2008 Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. All
rights reserved. Unauthorized copying and
distribution is a violation of law.
Vol. 1
Colours
(K).......................Black Type
(S).......................Silver Type
DVD Recorder
ORDER NO.DSD0806025CE
Model No.

1 Safety Precaution 4
1.1. General guidelines 4
2 Warning 5
2.1. Prevention of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) to
Electrostatic Sensitive (ES) Devices 5
2.2. Precaution of Laser Diode 6
2.3. Service caution based on legal restrictions 7
3 Service Navigation 8
3.1. Service Information 8
4 Specifications 9
5 Location of Controls and Components 10
5.1. Each Buttons 10
6 Operation Instructions 12
6.1. (DVD) Taking out the Disc from RAM-Drive Unit when the
Disc cannot be ejected by OPEN/CLOSE button 12
6.2. (VHS) Removing Cassette Tape manually 14
7 Service Mode 16
7.1. (DVD) Self-Diagnosis and Special Mode Setting 16
7.2. (VHS) Self-Diagnosis and Special Mode Setting 26
8 Service Fixture & Tools 30
9 Assembling and Disassembling Instructions 31
9.1. Disassembly Flow Chart 31
9.2. P.C.B. Positions 32
9.3. Caution with inserting cassette tape when disassembling
the unit 33
9.4. Top cover 34
9.5. Front Panel 34
9.6. Front Jack P.C.B., FL Drive P.C.B. 35
9.7. VHS Mechanism Unit 37
9.8. RAM/Digital P.C.B. Module 38
9.9. DV Jack P.C.B. 39
9.10. Rear Panel, Fan Motor 40
9.11. HDMI P.C.B. 40
9.12. Dig. Interface P.C.B. 41
9.13. Backend P.C.B. 41
9.14. Main P.C.B. 41
10 Measurements and Adjustments 42
10.1. Service Positions 42
10.2. Caution for Replacing Parts 45
10.3. (DVD) Standard Inspection Specifications after Making
Repairs 48
11 Block Diagram 51
11.1. Power Supply Block Diagram 51
11.2. Main P.C.B. Regulator Block Diagram 52
11.3. Analog Video (1/2) Block Diagram 53
11.4. Analog Video (2/2) Block Diagram 54
11.5. Analog Audio Block Diagram 55
11.6. D-IF/Timer Block Diagram 57
11.7. System Control & Servo Block Diagram 58
11.8. HDMI Block Diagram 59
12 Schematic Diagram 61
12.1. Interconnection Schematic Diagram 61
12.2. Power Supply Section (Dig. Interface P.C.B.(1/2))
Schematic Diagram (P) 63
12.3. Digital I/F (1/4) Section (Dig. Interface P.C.B.(2/2))
Schematic Diagram (IF) 65
12.4. Digital I/F (2/4) Section (Dig. Interface P.C.B.(2/2))
Schematic Diagram (IF) 66
12.5. Digital I/F (3/4) Section (Dig. Interface P.C.B.(2/2))
Schematic Diagram (IF) 67
12.6. Digital I/F (4/4) Section (Dig. Interface P.C.B.(2/2))
Schematic Diagram (IF) 68
12.7. Video Section (Main P.C.B.(1/5)) Schematic Diagram (V)
69
12.8. VHS Audio Section (Main P.C.B.(2/5)) Schematic Diagram
(A) 70
12.9. Syscon/Servo/Timer (1/4) Section (Main P.C.B.(3/5))
Schematic Diagram (S) 71
12.10. Syscon/Servo/Timer (2/4) Section (Main P.C.B.(3/5))
Schematic Diagram (S) 72
12.11. Syscon/Servo/Timer (3/4) Section (Main P.C.B.(3/5))
Schematic Diagram (S) 73
12.12. Syscon/Servo/Timer (4/4) Section (Main P.C.B.(3/5))
Schematic Diagram (S) 74
12.13. I/O Section (1/4) (Main P.C.B.(4/5)) Schematic Diagram
(AV) 76
12.14. I/O Section (2/4) (Main P.C.B.(4/5)) Schematic Diagram
(AV) 77
12.15. I/O Section (3/4) (Main P.C.B.(4/5)) Schematic Diagram
(AV) 78
12.16. I/O Section (4/4) (Main P.C.B.(4/5)) Schematic Diagram
(AV) 79
12.17. Tuner Section (Main P.C.B.(5/5)) Schematic Diagram (TU)
81
12.18. HDMI Schematic Diagram 82
12.19. FL Drive Schematic Diagram 83
12.20. DV Jack Schematic Diagram 84
12.21. Front Jack Schematic Diagram 84
13 Printed Circuit Board 85
13.1. Dig. Interface P.C.B. 85
13.2. Main P.C.B. 90
13.3. HDMI P.C.B. 95
CONTENTS
Page Page
2
DMR-EZ48VEB

13.4. FL Drive P.C.B. 96
13.5. Front Jack P.C.B. 97
13.6. DV Jack P.C.B. 97
14 Appendix for Schematic Diagram 99
14.1. Voltage and Waveform Chart 99
14.2. Abbreviations 107
15 Parts and Exploded Views 113
15.1. Exploded Views 113
15.2. Replacement Parts List 117
3
DMR-EZ48VEB
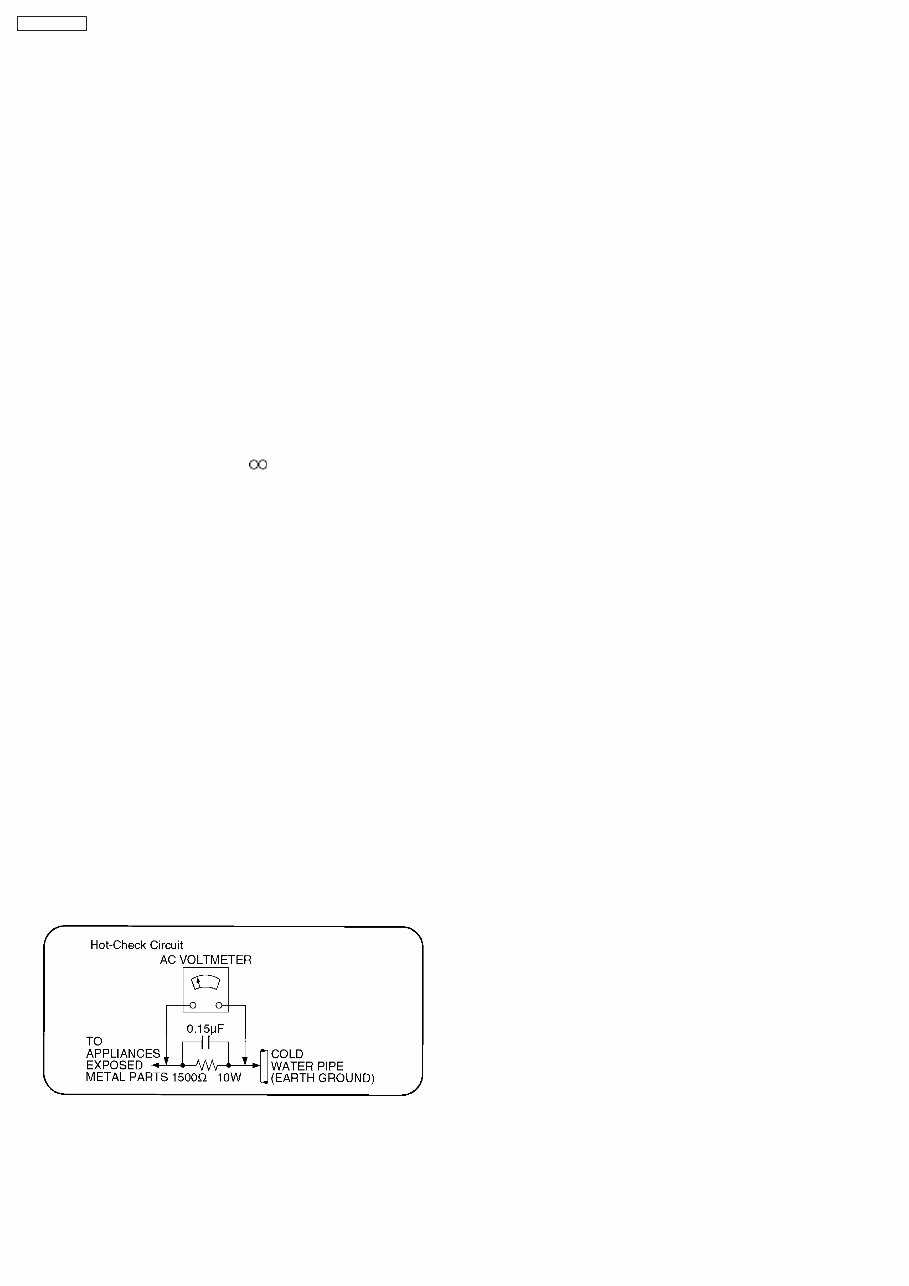
1.1.1. Leakage current cold check
1. Unplug the AC cord and connect a jumper between the two
prongs on the plug.
2. Measure the resistance value, with an ohmmeter, between
the jumpered AC plug and each exposed metallic cabinet
part on the equipment such as screwheads, connectors,
control shafts, etc. When the exposed metallic part has a
return path to the chassis, the reading should be between
1M and 5.2M.
When the exposed metal does not have a return path to the
chassis, the reading must be .
1.1.2. Leakage current hot check
(See Figure 1 .)
1. Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet. Do not use an
isolation transformer for this check.
2. Connect a 1.5k, 10 watts resistor, in parallel with a 0.15μF
capacitors, between each exposed metallic part on the set
and a good earth ground such as a water pipe, as shown in
Figure 1.
3. Use an AC voltmeter, with 1000 ohms/volt or more
sensitivity, to measure the potential across the resistor.
4. Check each exposed metallic part, and measure the
voltage at each point.
5. Reverse the AC plug in the AC outlet and repeat each of the
above measurements.
6. The potential at any point should not exceed 0.75 volts
RMS. A leakage current tester (Simpson Model 229 or
equivalent) may be used to make the hot checks, leakage
current must not exceed 1/2 milliampere. In case a
measurement is outside of the limits specified, there is a
possibility of a shock hazard, and the equipment should be
repaired and rechecked before it is returned to the
customer.
Figure 1
1 Safety Precaution
1.1. General guidelines
1. When servicing, observe the original lead dress. If a short circuit is found, replace all parts which have been overheated or
damaged by the short circuit.
2. After servicing, see to it that all the protective devices such as insulation barriers, insulation papers shields are properly
installed.
3. After servicing, make the following leakage current checks to prevent the customer from being exposed to shock hazards.
4
DMR-EZ48VEB

2 Warning
2.1. Prevention of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) to Electrostatic Sensitive
(ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity. Such components commonly are called
Electrostatic Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistor-sand
semiconductor "chip" components. The following techniques should be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage
caused by electrostatic discharge (ESD).
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off any ESD on your
body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available discharging ESD wrist strap,
which should be removed for potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as
aluminum foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder removal device. Some solder removal devices not classified as "anti-static (ESD protected)" can
generate electrical charge sufficient to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective package until immediately before you are ready to install it. (Most
replacement ES devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum foil or comparable
conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material
to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installed.
Caution
Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement ES devices. (Otherwise harmless motion such as the
brushing together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity sufficient
to damage an ES device).
5
DMR-EZ48VEB

2.2. Precaution of Laser Diode
6
DMR-EZ48VEB

2.3. Service caution based on legal restrictions
2.3.1. General description about Lead Free Solder (PbF)
The lead free solder has been used in the mounting process of all electrical components on the printed circuit boards used for this
equipment in considering the globally environmental conservation.
The normal solder is the alloy of tin (Sn) and lead (Pb). On the other hand, the lead free solder is the alloy mainly consists of tin
(Sn), silver (Ag) and Copper (Cu), and the melting point of the lead free solder is higher approx.30 degrees C (86°F) more than that
of the normal solder.
Definition of PCB Lead Free Solder being used
The letter of “PbF” is printed either foil side or components side on the PCB using the lead free solder.
(See right figure)
Service caution for repair work using Lead Free Solder (PbF)
· The lead free solder has to be used when repairing the equipment for which the lead free solder is used.
(Definition: The letter of “PbF” is printed on the PCB using the lead free solder.)
· To put lead free solder, it should be well molten and mixed with the original lead free solder.
· Remove the remaining lead free solder on the PCB cleanly for soldering of the new IC.
· Since the melting point of the lead free solder is higher than that of the normal lead solder, it takes the longer time to melt
the lead free solder.
· Use the soldering iron (more than 70W) equipped with the temperature control after setting the temperature at 350±30
degrees C (662±86°F).
Recommended Lead Free Solder (Service Parts Route.)
· The following 3 types of lead free solder are available through the service parts route.
RFKZ03D01K-----------(0.3mm 100g Reel)
RFKZ06D01K-----------(0.6mm 100g Reel)
RFKZ10D01K-----------(1.0mm 100g Reel)
Note
* Ingredient: tin (Sn), 96.5%, silver (Ag) 3.0%, Copper (Cu) 0.5%, Cobalt (Co) / Germanium (Ge) 0.1 to 0.3%
7
DMR-EZ48VEB

3 Service Navigation
3.1. Service Information
8
DMR-EZ48VEB
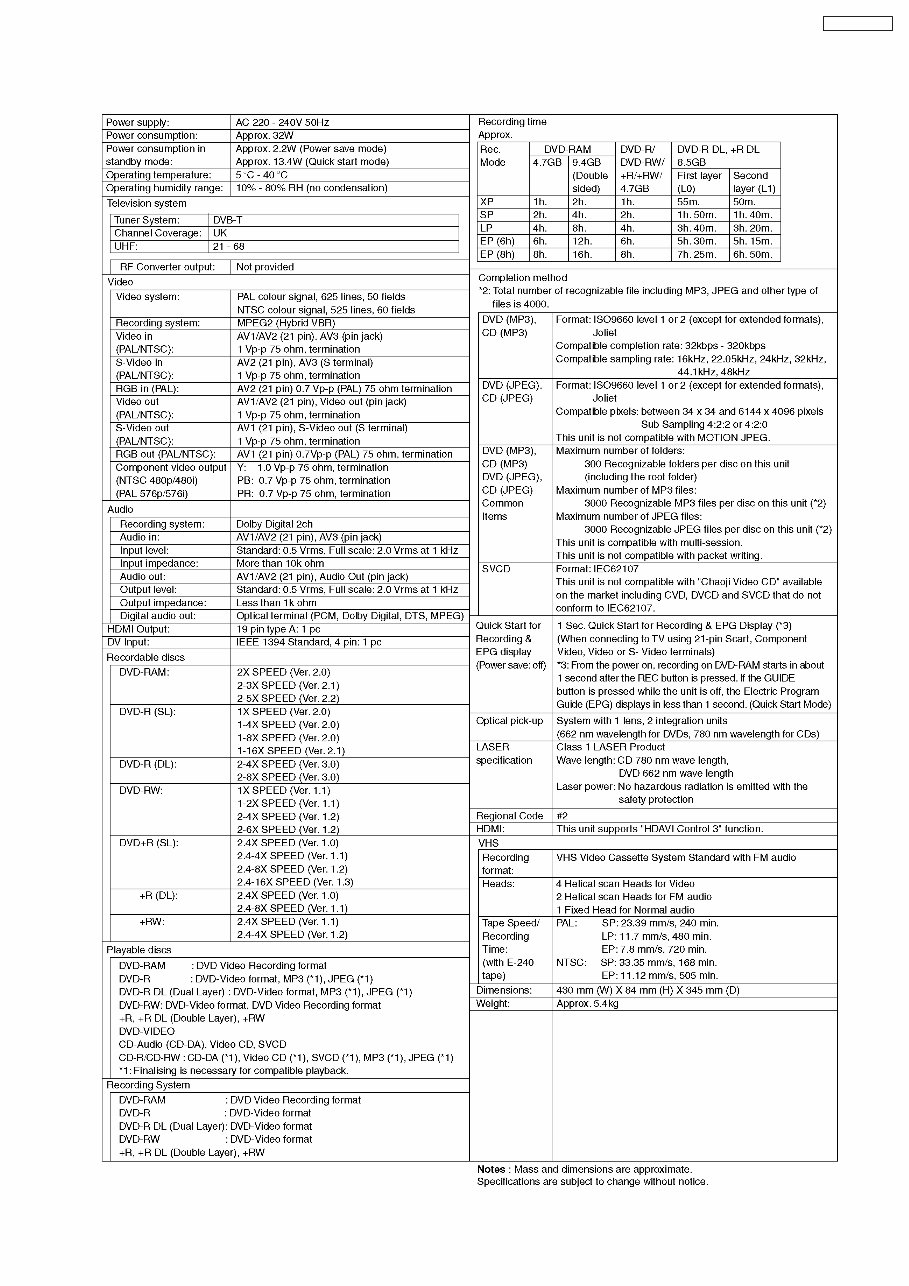
4 Specifications
9
DMR-EZ48VEB
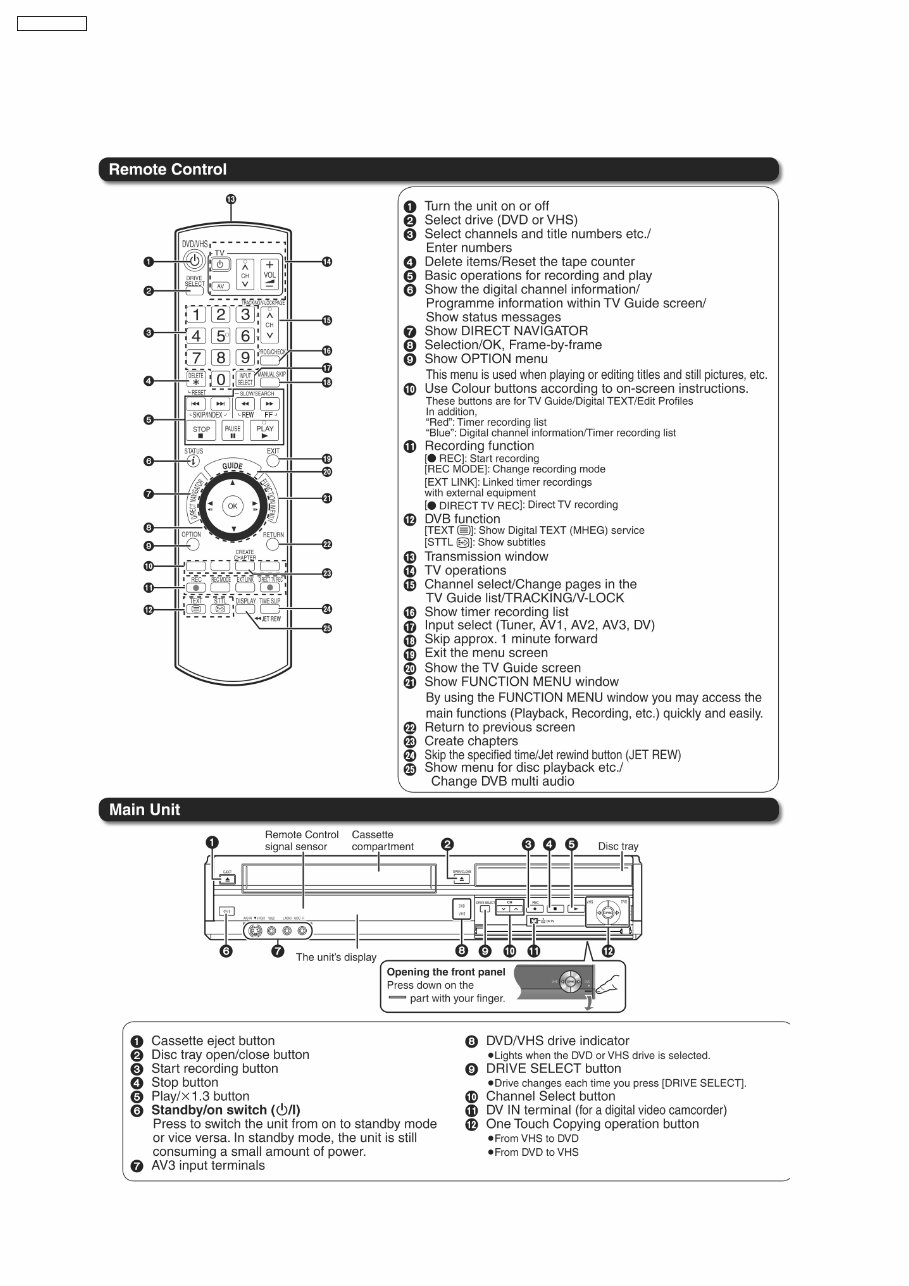
5 Location of Controls and Components
5.1. Each Buttons
10
DMR-EZ48VEB
You're Reading a Preview
What's Included?
Fast Download Speeds
Online & Offline Access
Access PDF Contents & Bookmarks
Full Search Facility
Print one or all pages of your manual
$35.99
$46.99
Viewed 72 Times Today


Loading...
Secure transaction
What's Included?
Fast Download Speeds
Online & Offline Access
Access PDF Contents & Bookmarks
Full Search Facility
Print one or all pages of your manual
$35.99
$46.99
This official service and repair manual is an essential resource for professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts alike. It is utilized by certified Panasonic technicians and service employees, providing in-depth information on safety and service precautions, specifications and operations, service modes, disassembly and assembly instructions, measurements and adjustments, block diagrams, schematic diagrams, printed circuit boards, exploded views, and a parts list catalog.
It is available in English and comes in a format that allows for instant access without any shipping fees or waiting on postal delivery. With 128 pages, this manual is created in the highest resolution, ensuring excellent quality when printed.




