
1948-1952 Ford 8N Tractor Service Repair Factory Manual
What's Included?
Fast Download Speeds
Online & Offline Access
Access PDF Contents & Bookmarks
Full Search Facility
Print one or all pages of your manual

INDEX (By Starting Paragraph)
Models
9N-2N 8N
BELT PULLEY 142 142
BRAKES
Adjustment 135 136
Brake Shoes 137 138
CLUTCH
Adjustment 97 98
Overhaul 101 101
Tractor Split 99 100
Troubleshooting 96 96
COOLING SYSTEM
Radiator 59 59
Thermostat 63 63
Water Pump 60 60
DIFFERENTL\L, BEVEL GEARS AND REAR
AXLES
Axles and Bearings 129 132
Differential 124 124
Main Drive Bevel Gears 127 127
Tractor Rear Split 126 126
ELECTRICAL AND IGNITION SYSTEM
Battery Ignition 85 85, 88
Charging System 64 64
Generator and Regulator 65 65
Generator Overhaul. 73 73
Ignition System 84 84
Magneto Ignition System (2N) . 92
Starting Motor and Switch .... 81 81
FRONT AXLE
Axle Center Member and
King Pin 12 12
Axle Front Support 13 13
Front Wheel Bearings 10 10
Spindle Bushings 11 H
Tread Width and Toe-In 9 9
FUEL SYSTEM
Carburetor Operation 48 48
Carburetor Overhaul 52 52
Troubleshooting 51 51
ENGINE
Assembly, R&R 21 21
Compression Pressure 22 22
Connecting Rod
and Piston Units 33 33
Models
9N-2N 8N
Connecting Rods and Bearings . 39
Camshaft 32
Crankshaft and Main Bearings. 40
Crankshaft Oil Seals 43
Cyhnder Head 23
Flywheel 44
Oil Pan 45
Oil Pump 46
Piston Pins 35
Piston Rings 34
Sleeves and Pistons 36
Timing Gears and Cover 29
Valves 24, 25
Valve Guides and Springs ..... 27
Valve PusTi Rods. . 28
Valve Seats 26
GOVERNOR
Adjustment 57
R&R and Overhaul 58
Troubleshooting 56
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
Adjustments 149
Hydraulic Lift Operation 143
Hydraulic Pump R&R and Test. 160
Lift Cover 156
Pump Overhaul 169
Troubleshooting 155
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE
Lubrication 2 2
Maintenance Procedures 4 4
Scheduled Maintenance 1 1
39
32
40
43
23
44
45
46
35
34
36
29
24,25
27
28
26
57
58
56
151
143
160
158
162
155
PART NUMBERS 175 175
POWER TAKE-OFF
Pto Shifter Unit 141 141
Output Shaft 139, 140 140
SHERMAN TRANSMISSION
Overhaul 105 105
Remove and Reinstall 103 103
STANDARD TRANSMISSION
Overhaul HO 117
Remove and Reinstall 109 109
STEERING SYSTEM
Steering Gear Adjustment 14 16,18
Steering Gear R&R
and Overhaul 15 17, 19
DUAL DIMENSIONS
This service manual provides specifications in both U.S. Customary and Metric (SI) systems of
measurement. The first specification is given in the measuring system perceived by us to be the
preferred system when servicing a particular component, whiie the second specification (given in
parenthesis) is the converted measurement. For instance, a specification of 0.011 inch (0.28 mm)
wouid indicate that we feel the preferred measurement in this instance is the U.S. Customary system
of measurement and the Metric equivalent of 0.011 inch is 0.28 mm.
CONDENSED SERVICE DATA
Models
9N,2N,8N
GENERAL
Engine Make Own
Engine Type L-Head
Number of Cylinders 4
Bore 3.187 in.
(80.96 mm)
Stroke 3.750 in.
(95.25 mm)
Displacement 119.7 cu. in.
(1.9 L)
Power Rating at Belt Pulley—Maximum
9N, 2N 23.6 hp
(17.6 kW)
8N 27.3 hp
(20.4 kW)
Power Rating at Drawbar—Maximum
9N, 2N 16.3 hp
(12.2 kW)
8N 23.2 hp
(17.3 kW)
Compression Ratio—Gasoline:
9N, 2N, Early 8N 6:1
Later 8N 6.5:1
Pistons Removed From Above
Main Bearings, Number of 3
Main Bearings, Adjustable? No
. Rod Bearings, Adjustable? No
Cylinder Sleeves, Dry, Wet? Dry
Production Cylinder Sleeves-
Material (8N Prior to S.N. 433578,
9N,2N) Steel
Material (8N After S.N. 433577) Cast Iron
Service Cylinder Sleeves-
Material (All Models) Cast Iron
Generator Make Own
Maximum Output 20 Amps
Starter Make Own
Type 6-Volt
Battery ^
Type 6-Volt
Ground Terminal . Positive
Models
. 9N,2N,8N
Tire Size^—Standard
Front 4-19 4-ply
Rear:
9N (Early) 8-32 4-ply
9N (Late)-2N-8N 10-28 4-ply
Transmission
Type Constant Mesh
Forward Speeds (9N, 2N) 3
Forward Speeds (8N) 4
Hydraulic Pump
Type Scotch Yoke Piston
Capacity @ 2000 Engine Rpm . . . 2.85 Gal./min.
(10.8L/min.)
TUNE-UP
Firing Order 1-2-4-3
Valve Tappet Gap (Cold)
Inlet. 0.010-0.012 in.
(0.26-0.30 mm)
Exhaust 0.014-0.016 in.
(0.36-0.40 mm)
Valve Face Angle
Inlet and Exhaust 45°
Valve Seat Angle
Inlet and Exhaust 45°
Ignition Distributor Make Own
Distributor Model
8N Prior to S.N. 263844, 9N, 2N) 9N12100
8N After S.N. 263843 8N12127
Breaker Point Gap
Angle Mounted Distributor
No. 8N12127 0.025 in.
(0.63 mm)
Face Mounted Distributor
No. 9N12000 0.015 in.
(0.38 mm)
Retarded Timing
8N Prior to S.N. 263844, 9N, 2N TDC
8N After S.N. 263843 4° BTDC
Advanced Timing
8N Prior to S.N. 263844, 9N, 2N 25° BTDC
Advanced Timing
8N After S.N. 263843 ........ .. ! . . . 17° BTDC
DUAL DIMENSIONS
This service manual provides specifications in both U.S. Customary and Metric (SI) systems of
measurement. The first specification is given in the measuring system perceived by us to be the
preferred system when servicing a particular component, whiie the second specification (given in
parenthesis) is the converted measurement. For instance, a specification of 0.011 inch (0.28 mm)
wouid indicate that we feel the preferred measurement in this instance is the U.S. Customary system
of measurement and the Metric equivalent of 0.011 inch is 0.28 mm.
CONDENSED SERVICE DATA
Models
9N,2N,8N
GENERAL
Engine Make Own
Engine Type L-Head
Number of Cylinders 4
Bore 3.187 in.
(80.96 mm)
Stroke 3.750 in.
(95.25 mm)
Displacement 119.7 cu. in.
(1.9 L)
Power Rating at Belt Pulley—Maximum
9N, 2N 23.6 hp
(17.6 kW)
8N 27.3 hp
(20.4 kW)
Power Rating at Drawbar—Maximum
9N, 2N 16.3 hp
(12.2 kW)
8N 23.2 hp
(17.3 kW)
Compression Ratio—Gasoline:
9N, 2N, Early 8N 6:1
Later 8N 6.5:1
Pistons Removed From Above
Main Bearings, Number of 3
Main Bearings, Adjustable? No
. Rod Bearings, Adjustable? No
Cylinder Sleeves, Dry, Wet? Dry
Production Cylinder Sleeves-
Material (8N Prior to S.N. 433578,
9N,2N) Steel
Material (8N After S.N. 433577) Cast Iron
Service Cylinder Sleeves-
Material (All Models) Cast Iron
Generator Make Own
Maximum Output 20 Amps
Starter Make Own
Type 6-Volt
Battery ^
Type 6-Volt
Ground Terminal . Positive
Models
. 9N,2N,8N
Tire Size^—Standard
Front 4-19 4-ply
Rear:
9N (Early) 8-32 4-ply
9N (Late)-2N-8N 10-28 4-ply
Transmission
Type Constant Mesh
Forward Speeds (9N, 2N) 3
Forward Speeds (8N) 4
Hydraulic Pump
Type Scotch Yoke Piston
Capacity @ 2000 Engine Rpm . . . 2.85 Gal./min.
(10.8L/min.)
TUNE-UP
Firing Order 1-2-4-3
Valve Tappet Gap (Cold)
Inlet. 0.010-0.012 in.
(0.26-0.30 mm)
Exhaust 0.014-0.016 in.
(0.36-0.40 mm)
Valve Face Angle
Inlet and Exhaust 45°
Valve Seat Angle
Inlet and Exhaust 45°
Ignition Distributor Make Own
Distributor Model
8N Prior to S.N. 263844, 9N, 2N) 9N12100
8N After S.N. 263843 8N12127
Breaker Point Gap
Angle Mounted Distributor
No. 8N12127 0.025 in.
(0.63 mm)
Face Mounted Distributor
No. 9N12000 0.015 in.
(0.38 mm)
Retarded Timing
8N Prior to S.N. 263844, 9N, 2N TDC
8N After S.N. 263843 4° BTDC
Advanced Timing
8N Prior to S.N. 263844, 9N, 2N 25° BTDC
Advanced Timing
8N After S.N. 263843 ........ .. ! . . . 17° BTDC

V / Models
V.:' • : 9N,2N,8N
TUNE-UP (Cont.)
Flywheel Timing Mark Indicating:
Retarded Timing (8N Prior to
S.N. 263844, 9N, 2N) None
Retarded Timing (8N After
S.N. 263843) 4° Line
Advanced Timing (8N Prior to
S.N. 263844, 9N, 2N) None
Advanced Timing (8N
After S.N. 263843) 17° Line
Distributor Governor Advance Curve. . . See Text
Spark Plug
Make Champion
Plug Model for Gasoline HIO
Electrode Gap 0.025-0.028 in.
(0.64-0.71 mm)
Carburetor
Make Marvel-Schebler
Carburetor Model See Text
Carburetor Float Setting %2 in.
(7 mm)
Carburetor Initial Adjustment
Idle Adjustment Needle 1 Turn Open
Main Jet Adjustment Needle 1 Tum Open
Engine Low Idle RPM 400
Engine High Idle RPM 2200
Belt Pulley RPM @ 2000 Engine RPM 1358
Pto RPM @ 1500 Engine RPM 545
Compression Pressure @ Cranking Speed
Minimum 90 psi
(620 kPa)
SIZES—CLEARANCES
Crankshaft Joumal Diameter 2.248-2.249 in.
(57.10-57.12 mm)
Crankpin Diameter .' 2.094 in.
(53.18 mm)
Camshaft Joumal Diameter 1.797 in.
(45.64 mm)
Piston Pin Diameter 0.7501-0.7504 in.
(19.05-19.06 mm)
Valve Stem Diameter
One-Piece Valve Guide 0.341-0.342 in.
(8.66 mm)
Models
9N,2N,8N
Two-Piece Valve Guide 0.3105-0.3115 in.
(7.89-7.91 mm)
Cam Follower (Push Rod) Diameter... 0.9995 in.
(25.38 mm)
Compression Ring Width 0.093 in.
(2.36 mm)
Oil Ring Width 0.187 in.
(4.75 mm)
Main Bearings Running
Clearance 0.001-0.003 in.
(0.025-0.076 mm)
Rod Bearings Running
Clearance 0.001-0.0035 in.
(0.025-0.089 mm)
Piston Skirt Clearance
Steel Pistons 0.0025-0.004 in.
(0.064-0.101 mm)
Aluminum Pistons 0.0015-0.0025 in.
(0.038-0.063 mm)
Camshaft Bearing Clearance 0.001-0.002 in.
(0.025-0.050 mm)
Cam Follower (Push Rod)
Running Clearance 0.0004-0.001 in.
(0.010-0.025 mm)
Crankshaft End Play 0.002-0.006 in.
(0.05-0.15 mm)
CAPACITIES
Coohng System 3 Gallons
(11.3 L)
Crankcase Oil (With Filter Change) 6 Quarts
(5.6 L)
Fuel Tank
Standard 9 Gallons
(34 L)
Reserve 1 Gallon
(3.8 L)
Transmission, Differential &
Hydraulic System 5 Gallons
(18.9 L)
Belt Pulley Housing V3 Quart
(0.3 L)
8
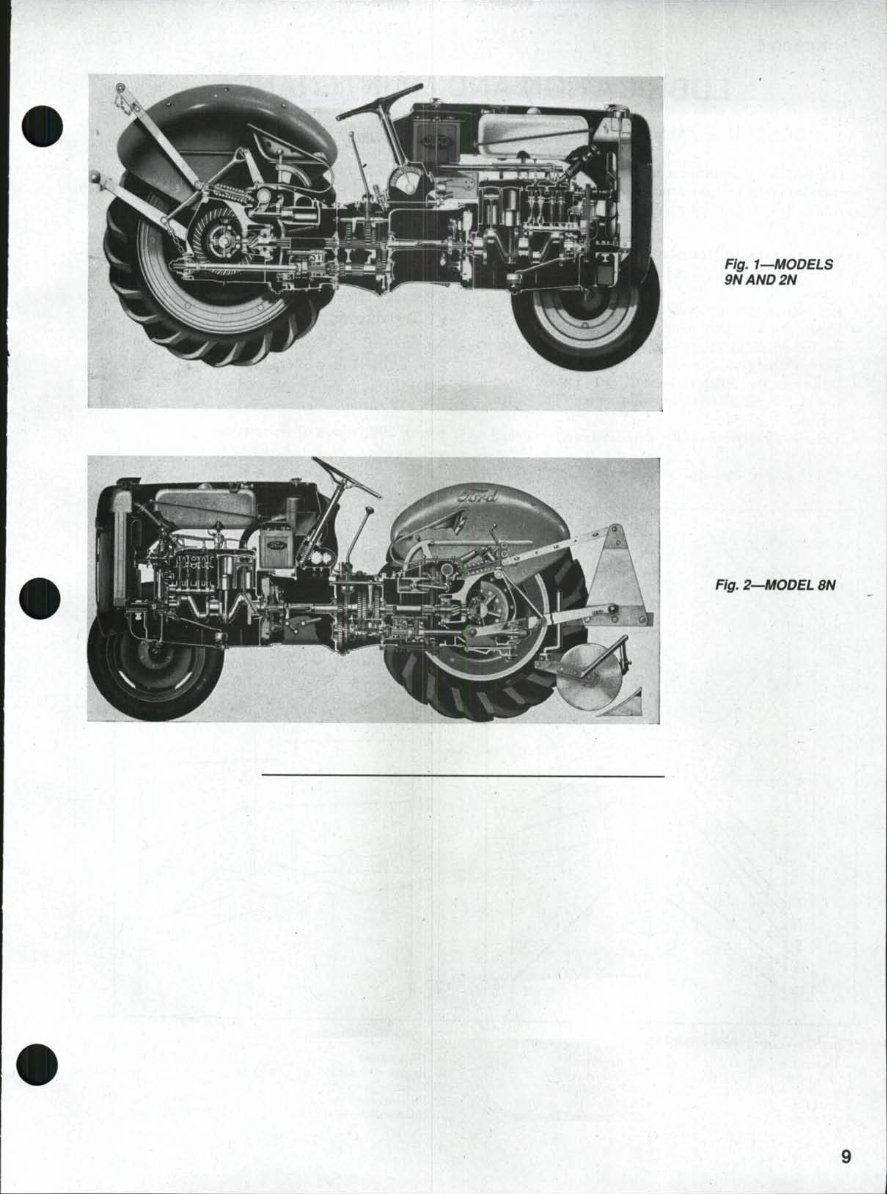
Fig, 1—MODELS
9NAND2N
Fig. 2—MODEL 8N
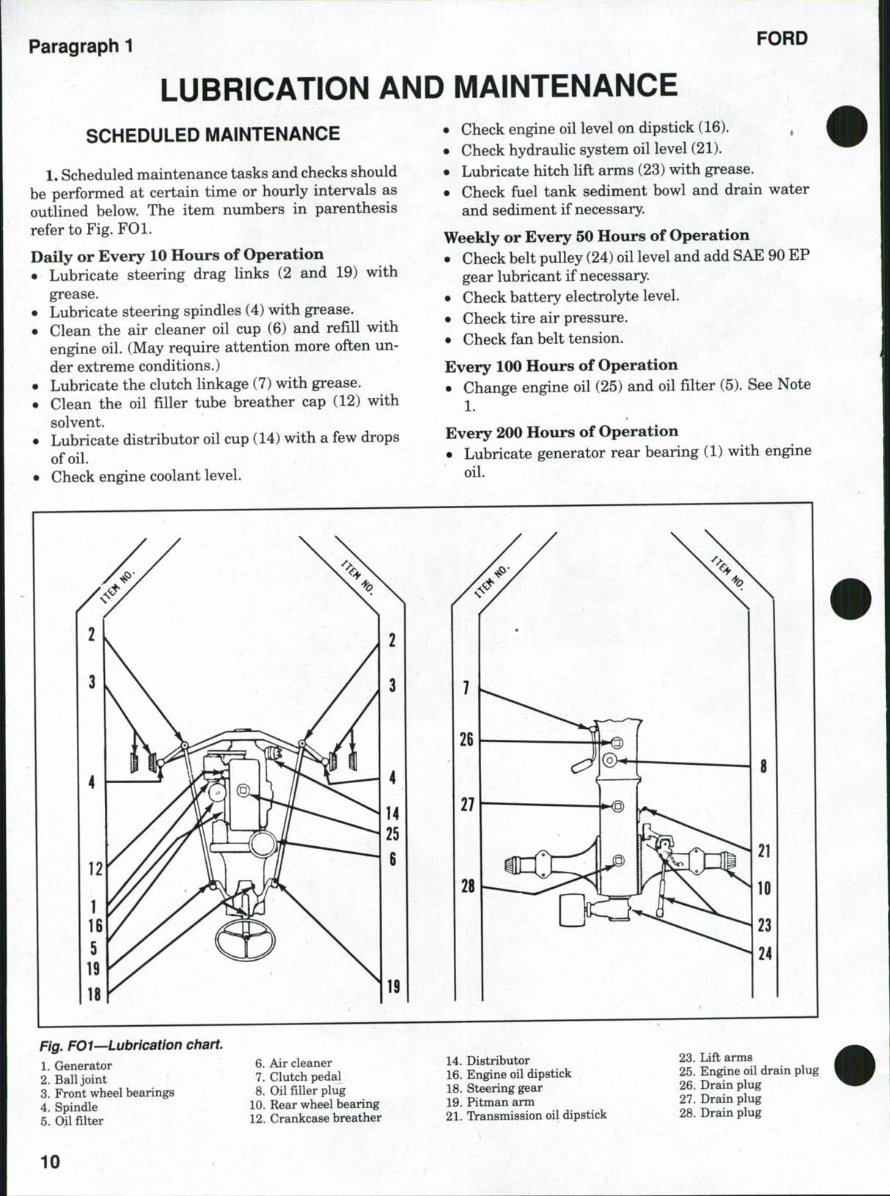
Paragraph 1
FORD
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE
SCHEDULED MAINTENANCE
1. Scheduled maintenance tasks and checks should
be performed at certain time or hourly intervals as
outlined below. The item numbers in parenthesis
refer to Fig. FOl.
Daily or Every 10 Hours of Operation
• Lubricate steering drag links (2 and 19) with
grease.
• Lubricate steering spindles (4) with grease.
• Clean the air cleaner oil cup (6) and refill with
engine oil. (May require attention more often un-
der extreme conditions.)
• Lubricate the clutch linkage (7) with grease.
• Clean the oil filler tube breather cap (12) with
solvent.
• Lubricate distributor oil cup (14) with a few drops
of oil.
• Check engine coolant level.
• Check engine oil level on dipstick (16). ,
• Check hydraulic system oil level (21).
• Lubricate hitch lift arms (23) Mdth grease.
• Check fuel tank sediment bowl and drain water
and sediment if necessary.
Weekly or Every 50 Hours of Operation
• Check belt pulley (24) oil level and add SAE 90 EP
gear lubricant if necessary.
• Check battery electrolyte level.
• Check tire air pressure.
• Check fan belt tension.
Every 100 Hours of Operation
• Change engine oil (25) and oil filter (5). See Note
1.
Every 200 Hours of Operation
• Lubricate generator rear bearing (1) with engine
oil.
Fig. FOl—Lubrication chart.
1. Grenerator
2. Ball joint
3. Front wheel bearings
4. Spindle
5. Oil filter ;
6. Air cleaner
7. Clutch pedal
8. Oil filler plug
10. Rear wheel bearing
12. Crankcase breather
14. Distributor
16. Engine oil dipstick
18. Steering gear
19. Pitman arm
21. Transmission oil dipstick
23. Lift arms
25. Engine oil drain plug
26. Drain plug
27. Drain plug
28. Drain plug
10

MODELS 9N, 2N & 8N ^^^ h
• Clean distributor cam (14) and apply new lubri-
cant to cam.
• Check steering gear (18) oil level and add SAE 90
EP gear lubricant if necessary. Fill to top of filler
plug opening in side of steering gear housing.
Yearly or Every 600 Hours of Operation
• Tune-up the engine.
• Clean and repack front wheel bearings (3).
• Remove and clean carburetor air cleaner housing
and filter element (6). See Note 2.
• Drain transmission, differential and hydraulic
system oil and refill with new oil.
• Drain and flush cooling system. Refill with new
coolant.
Every 1800 Hours of Operation
• Clean and repack rear wheel bearings (10).
NOTE 1 - If tractor is operated under any of the
following conditions, change the engine oii and oii
fiiter more frequently:
a. Extremeiy hot or coid temperatures
b. Sustained heavy loads
c. Extended low speed operation
d. Extremely dusty conditions
NOTE 2 - Under severe dust condition, remove
and ciean the carburetor air cieaner assembiy every
100 hours of operation.
LUBRICATION
Engine Oil Change Periods
2. The frequency of oil changes depends upon the
severity of operation. Under normal operation condi-
tions, engine oil should be changed every 100 hours
of operation. Under extreme conditions (dusty, high
Paragraphs 2-3
^ temperature and heavy loads), oil should be changed
more frequently.
The oil should be changed every 50 hours when
operating the tractor in below freezing temperatures.
Intermittent engine operation and idling should be
kept to a minimum' in cold weather to avoid dilution
of the oil. Low temperature operation promotes
sludging which can plug oil passages and cause the
formation of corrosive acids which result in rapid
engine wear. Run the engine until the oil is at normal
operating temperature prior to draining the oil. Re-
move the drain plug and allow the oil to drain for at
least 10 minutes.
The oil filter element, located in filter canister on
left side of the engine (Fig. F02), should be changed
at the same time as the oil. Always use new gaskets
when reinstalling the filter canister and tighten re-
taining bolt to 20-25 ft.-lbs. (27-34 N.m) torque. Do
not overtighten as canister may be distorted, result-
ing in oil leakage.
Crankcase oil capacity is 6 quarts (5.7 L) with a
filter change. Select a good quality oil with SAE
viscosity grade suitable for the ambient temperature.
In the summer, consider the highest expected tem-
perature. In the winter, the oil must be thin enough
to permit easy starting.
Transmission, Differentiai and
Hydraulic Oii
3. On 9N, 2N and 8N tractors, the transmission and
differential housings serve as a common sump for the
lubricating and hydraulic system fiuid. The fiuid
level is checked by removing the level check plug
located on the lower right side of the transmission
housing on some early models, or by a dipstick located
in the inspection plate on right side of differential
housing on later models (Fig. F03).
On all models, the lubricating and hydraulic fiuid
should be changed every 600 hours of operation or
Fig. FO2—View of ieft side of 8N engine.
Fig. FO3—A dipstick, iocated in inspection cover, is used
to checii transmission oii ievei.
11

Paragraphs 4-6
FORD
Fig. F04—Transmission oil filler piug (8) is located on the
transmission cover (9N shown).
once a year, whichever comes first. Refer to Fig. FOl
for location of drain plugs (26, 27 and 28) and to Fig.
F04 for location offillerplug (8). The fiuid should be
warm when it is drained, and all drain plugs should
be removed on those models which have a common
housing.
Fluid capacity is approximately 5 gallons (19 L) on
9N, 2N, and 8N tractors. The recommended fiuid for
use in all models is Ford M2C 134-D hydraulic fiuid.
It is also permissible to use extreme pressure gear
lubricant in the transmission, differential and hy-
draulic system. Use SAE 90 EP gear oil if air tem-
perature will be above 32° F (0° C) and SAE 80 EP
gear oil if air temperature will be below 32° F (0° C).
MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Crankcase Ventilation
4. The engine crankcase is vented to the atmos-
phere to remove water vapor, gasoline vapor and
blowby products which can cause deterioration of the
oil and the corrosion of engine components. The
crankcase is vented through the oil filler tube
breather cap (Fig. F02). If the crankcase ventilation
system becomes restricted, the pressure in the crank-
case will rise above normal. Higher than normal
crankcase pressure may result in abnormal oil con-
sumption and external oil leakage at the crankshaft
seals.
The oil filler cap should be cleaned in suitable
solvent after every 10 hours of operation.
Fuei System
5. To clean the fuel tank sediment bowl (Fig. F05),
tum fuel shut-off valve clockwise to closed position.
COVER ASSEMBLY
SCREEN
GASKET-
CLAMP WIRE
AND SCREW
ASSEMBLY
VALVE STEM
Fig. F05—Exploded view of fuei shut-off vaive and sedi-
ment bowl assembly.
Loosen sediment bowl retaining nut, move retaining
wire clamp sideways and remove the bowl. Clean the
bowl with a clean cloth. Remove and clean the screen
located in the bowl cover.
A strainer screen, attached to the top of sediment
bowl cover, is located inside the fuel tank. In order to
clean this screen it is first necessary to drain the fiiel
from the tank, then remove the cover assembly from
the bottom of fuel tank.
Afuel strainer screen is also located in the fuel inlet
elbow of the carburetor. The screen should be re-
moved and cleaned periodically. The screen should
also be cleaned if there is an unusually large accumu-
lation of sediment in the fuel sediment bowl, or if
there is an indication that not enough fuel is reaching
the carburetor.
NOTE: If an excessive amount of dirt or water
quickly accumulates in the sediment bowl, the fuei
tank shouid be removed, drained and cleaned. Also,
the source of the contamination must be found and
corrected.
Carburetor Air Cieaner
6. An oil bath type air cleaner is used on all models
(6—Fig. F06). Air is drawn into the air cleaner and
directed downward toward the oil in the cup attached
to the bottom of the air cleaner body, then upward
through the filtering element into the carburetor.
Heavy particles of dirt are trapped by the oil in the
cup, smaller particles not retained in the oil cup are
screened out by the filter element in the air cleaner
body. If the oil in the cup becomes thick and gritty, the
air cleaner filter element will become restricted and
cause a drop in the volume of air reaching the engine.
12

iViODELS 9N, 2N & 8N
Paragraph 7
Fig. FO&-~Air cleaner (6) is mounted on right side of
tractor on ail models. Air cleaner cup shouid be fiiied with
ciean engine oil to oii level marii (M).
resulting in loss of power and excessive fuel consump-
tion.
The air intake on 9N and 2N tractors is beneath
the hood and subjected to a sort of "dust trap" which
has been corrected by most operators with the addi-
tion of an "Air Cleaner Extension" which raises the
air intake above the hood. The air cleaner extension
was available as a dealer option.
On the 8N tractor, a screened breather entrance is
located on the outside of the right rear comer of the
hood. A centrifugal type (Cyclone) attachment (31—
Fig. F06) was made available for 8N tractors which
whirled the incoming air and collected the dry dust
in a glass container where it could be emptied as the
container became full.
The air cleaner cup should be removed and in-
spected every ten hours of operation, or more often
under extremely dusty conditions. If oil in the cup is
dirty, clean the cup and refill with fresh engine oil
(same viscosity as used in engine crankcase) to the
full mark (M—Fig. F06) indicated on the cup.
Every 600 hours of operation, or more often under
dusty conditions, remove the complete air cleaner
from the tractor and wash the air cleaner body and
filter element with a suitable solvent. Dry the filter
element, then coat with light weight engine oil. Refill
the oil cup to proper level with engine oil and reinstall
the air cleaner assembly.
Failure to properly maintain the air cleaner will
result in poor engine performance and premature
wear of the engine.
Cooiing System
7. A pressure-type cooling system is used on 2N and
8N models, which means that more heat is required
to make the coolant boil than if the system were not
under pressure. The radiator is sealed with a cap that
contains a pressure valve and a vacuum valve.
The pressure valve in the radiator cap maintains
cooHng system pressure at 3.5 to 4.5 psi (24-31 kPa),
raising the boiling point of the coolant many degrees.
As the coolant heats, it expands, raising the pressure
in the system. The vacuum valve in the cap admits
displaced air when the engine is shut off, preventing
damage to the system. When the system is operating
properly, the air in the upper tank expands and
contracts protecting the system from damage.
CAUTiON: The radiator cap shouid never be re-
moved when the engine is hot. However, if this is
unavoidabie, cover the cap with a thick cioth or wear
heavy ieather gioves. Siowiy turn the cap counter-
ciockwise against the first stop (about V4 turn). Let
ail pressure (hot coolant and steam) escape, then
depress the cap and turn counterciockwise to re-
move. If the cap is removed too soon, scalding
coolant may escape and cause a serious burn.
The coolant level should be checked at the begin-
ning of the day when the engine is cold. Maintain the
coolant level slightly below the bottom of the radiator
filler neck to allow for expansion of the coolant when
it reaches normal operating temperature.
Check the condition of the coolant. If it is dirty or
rusty, drain the radiator and cylinder block and re-
move the thermostat. Clean and reverse fiush the
radiator and engine block, and refill with fresh cool-
ant.
It is recommended that a mixture of clean water
and ethylene glycol antifreeze be used as a coolant in
summer as well as winter. Ethylene glycol antifreeze
not only protects the coolant from freezing in cold
weather, it also increases the coolant boiling point
above that of plain water to reduce coolant loss during
operation in hot weather. Ethylene glycol antifreeze
also contains additives to inhibit the formation of
corrosion and rust in the cooling system. Capacity of
cooling system is 12 quarts (11.3 L) for 9N, 2N and
8N models.
If the temperature does not fall below the freezing
point, plain water can be used in the cooling system;
however, the cooling system should be treated with
rust and corrosion inhibitor. If the water supply con-
tains lime or alkali, it is recommended that distilled
water or rain water be used for a coolant. Deposits
caused by lime or alkali water will quickly build up
on the engine coolant passages which will eventually
result in overheating and possible engine damage.
13

Paragraphs 8-9
FORD
Fan Beit Tension
8. The fan belt tension is adjusted by changing the
position of the generator. See Fig. F07. The belt
tension is correct when the belt can be defiected V2
inch (13 mm) with moderate thumb pressure.
NOTE: The belt should be cool when tension is
adjusted.
A new belt will stretch slightly during the first few
hours of operation. When a new fan belt is installed,
operate the engine for about two hours to "run in" the
belt. Stop the engine then check and adjust the ten-
sion if necessary.
Do not overtighten the fan belt as premature wear
of the generator and water pump bearings may re-
sult. If belt tension is too loose, belt slippage may
occur, resulting in an overheated engine and low
generator output.
Fig. FOl—Change position of generator to adjust fan belt
tension.
FRONT AXLE
TREAD WiDTH AND TOE-iN
9. ADJUSTMENT. The front axle is constructed in
three sections and may be adjusted to vary the tread
width from 48 inches (122 cm) to 76 inches (193 cm).
See Figs. F08 and F09. Be sure to leave one or more
open holes between the bolts attaching the axle ex-
tension to axle center member when changing the
tread width. Note that the 76-inch (193 cm) tread
width spacing is obtained by setting the axle for
68-inch (173 cm) tread and reversing the front
wheels. ••?-•..
The rear wheel tread width settings can be ad-
justed to match the front tread width by changing the
position of the steel discs and wheel rims. The rear
tread width can be varied from 48 inches (122 cm) to
76 inches (193 cm) by installing wheel disks in either
a convex or concave position and/or by installing rims
on the disks in any of four different locations as shown
in Fig. FOIO.
NOTE: When making rear wheel tread width ad-
justments, be sure that arrow on the sidewail of the
Wheel Alignment Marks
Lock Nut
Turn Buckle
Lock Nut
Lock Nut
Turn
Buckle
Lock Nut
flg^ FO8—Front axle as used on 8N
tractors. Note hole spacing of tread
adjusting boits.
14
You're Reading a Preview
What's Included?
Fast Download Speeds
Online & Offline Access
Access PDF Contents & Bookmarks
Full Search Facility
Print one or all pages of your manual
$31.99
Viewed 18 Times Today


Loading...
Secure transaction
What's Included?
Fast Download Speeds
Online & Offline Access
Access PDF Contents & Bookmarks
Full Search Facility
Print one or all pages of your manual
$31.99
This Service Manual is an essential resource for anyone in need of immediate repair for the 1948-1952 Ford 8N Tractor. It contains comprehensive technical data, diagrams, and a complete list of parts, making it indispensable for professional mechanics and DIY enthusiasts alike.
- Description and Specifications
- Steering Gear
- Transmission
- Hydraulic System
- Rear Axle
- Power Take-off
- Belt Pulley
The manual is available in PDF format, compatible with all versions of Windows and Mac, and is presented in English. It can be easily accessed using Adobe Reader. Whether you take it into the garage or use it for cost-saving DIY repairs, this manual provides step-by-step instructions suitable for all skill levels.



